本文介绍了VMProtect在.NET程序集保护中的Mutation保护,以及如何使用控制流分析技术将它还原。
前言
这是.NET下VMProtect的反混淆,不是C++
VMProtect v3.4增加了对.NET程序的支持,我知道的功能有反调试,反Dump,Mutation(变异),Virtualization(虚拟化)。Virtualization确实强,我搞不定,不过大概看懂结构了,可能写工具自动重命名一下可以看得更明白,强度可能还是不如KoiVM。不过Mutation还是比较好搞定的,一种类似控制流混淆的东西,或者可以说是与控制流有关的常量加密。
分析
由于VMProtect Demo版本加壳的程序只能在自己电脑上运行,所以我自己写了个.NET样本。
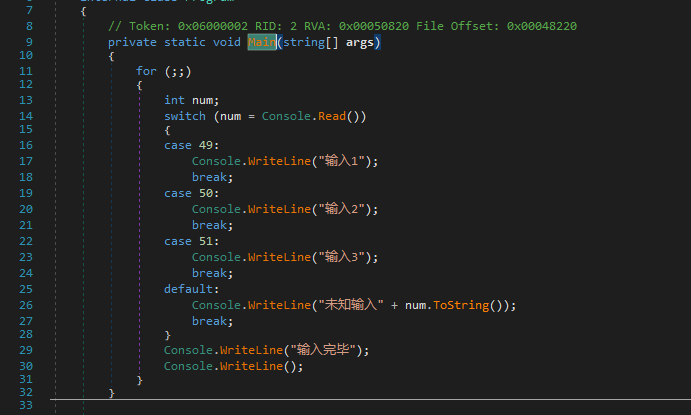
然后加壳,编译模式选择Mutation。用dnSpy打开,找到自己加壳的方法。可以发现有很多循环,这些循环是混淆器生成的。
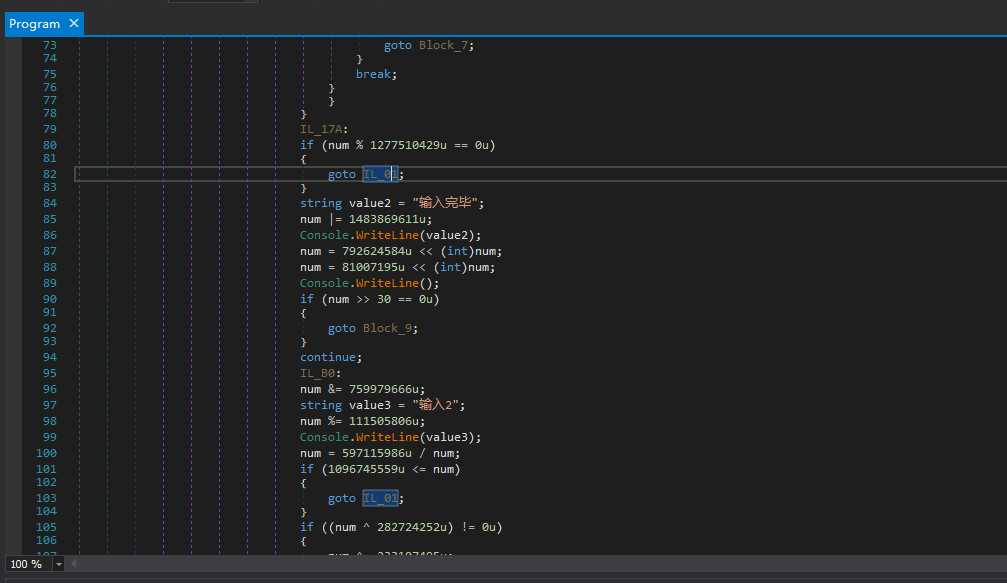
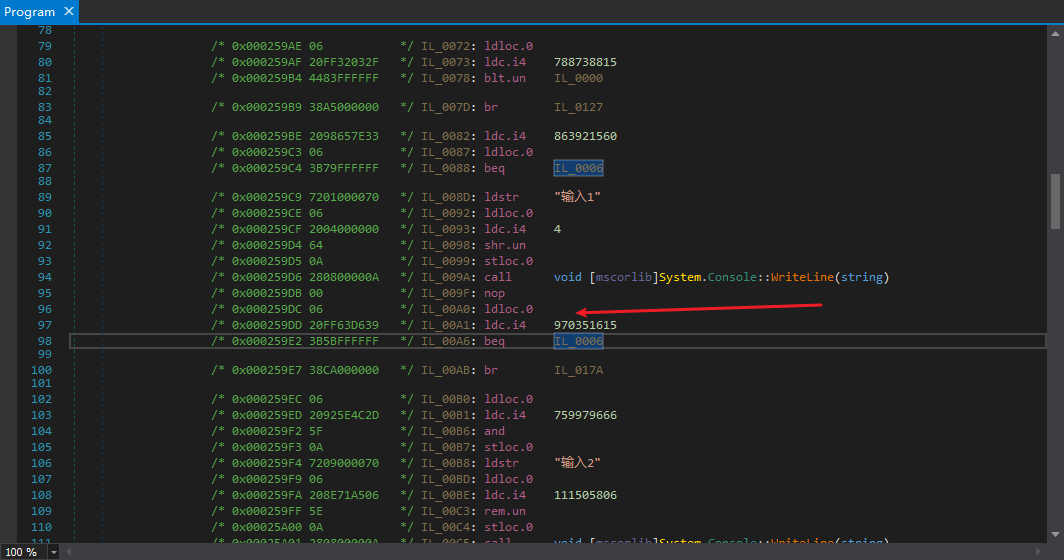
仔细观察,我们可以发现混淆比较单一,变量num是可以称为Context(上下文),执行一条指令,上下文就会自己更新一次。为什么我会选一个有switch语句的样本来加壳,因为我们需要知道进入不同的基本块,再转移到同一个基本块时,上下文是不是相同的(一般来说是相同的,因为我也想不出有不同的情况…)。
可能这样说不太容易明白,我直接调试,可以更明白些。样本中的每个case块对应了刚才说的不同的基本块,最终都会转移到同一个基本块,也就是”Console.WriteLine(“输入完毕”)”开始的这个基本块。所以我们在这个基本块下断点。
我们分别输入不同的数字,让switch语句跳转到不同的case块,看看是不是最终执行到”Console.WriteLine(“输入完毕”)”时,num的值是相同的。
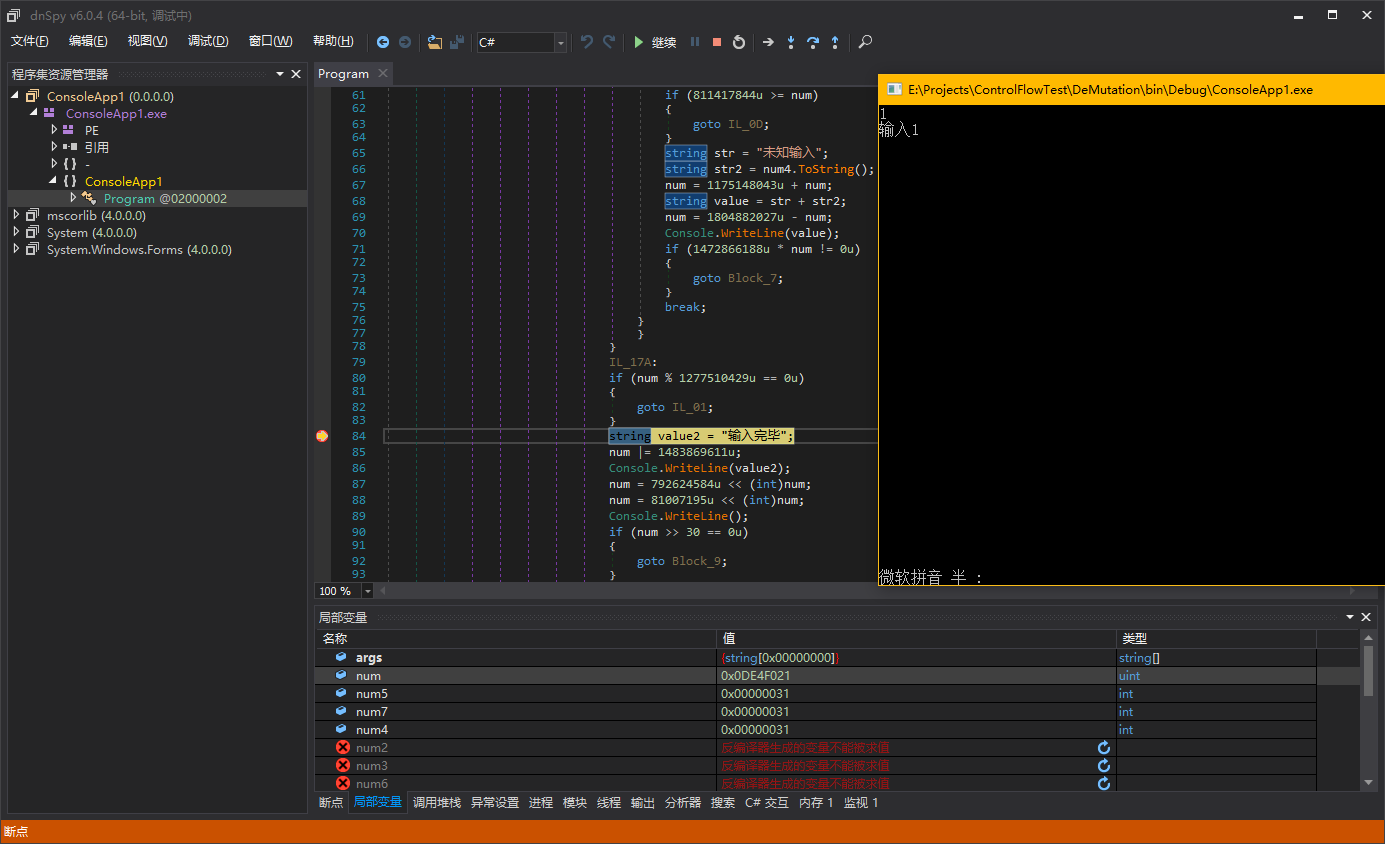
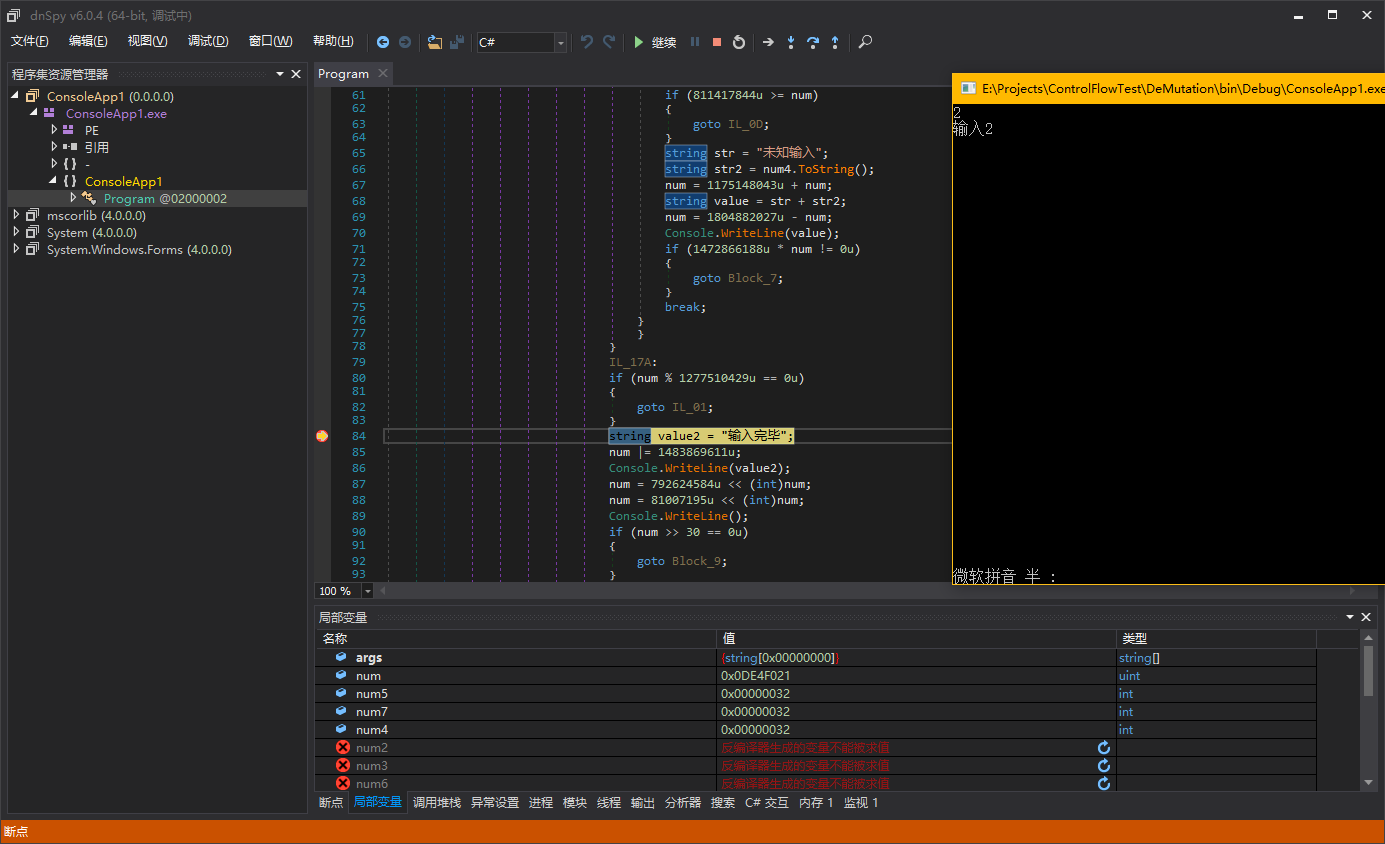
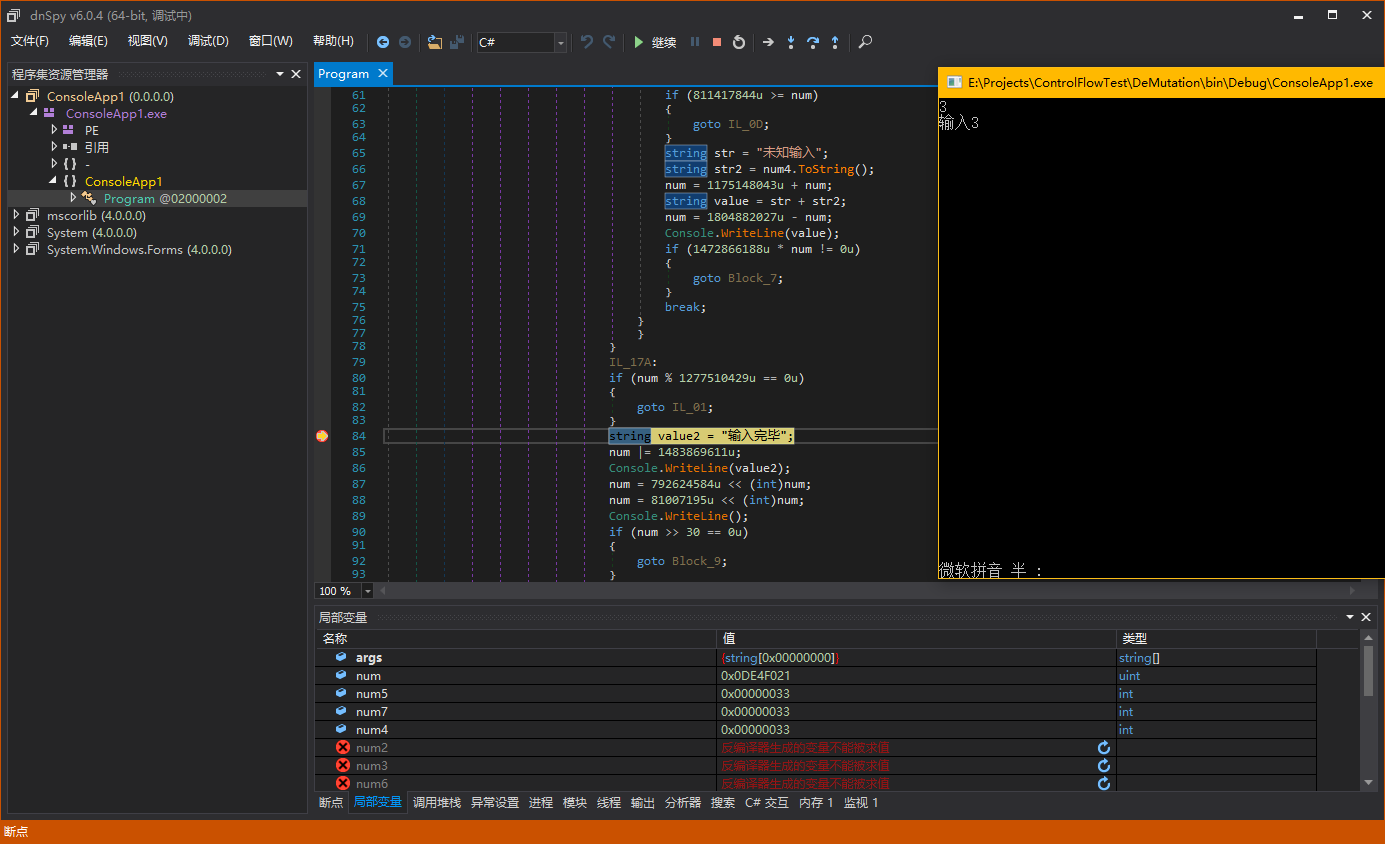
这样,我们的猜想是正确的,Mutation的宏观结构我们了解清楚了,可以进行下一步分析。
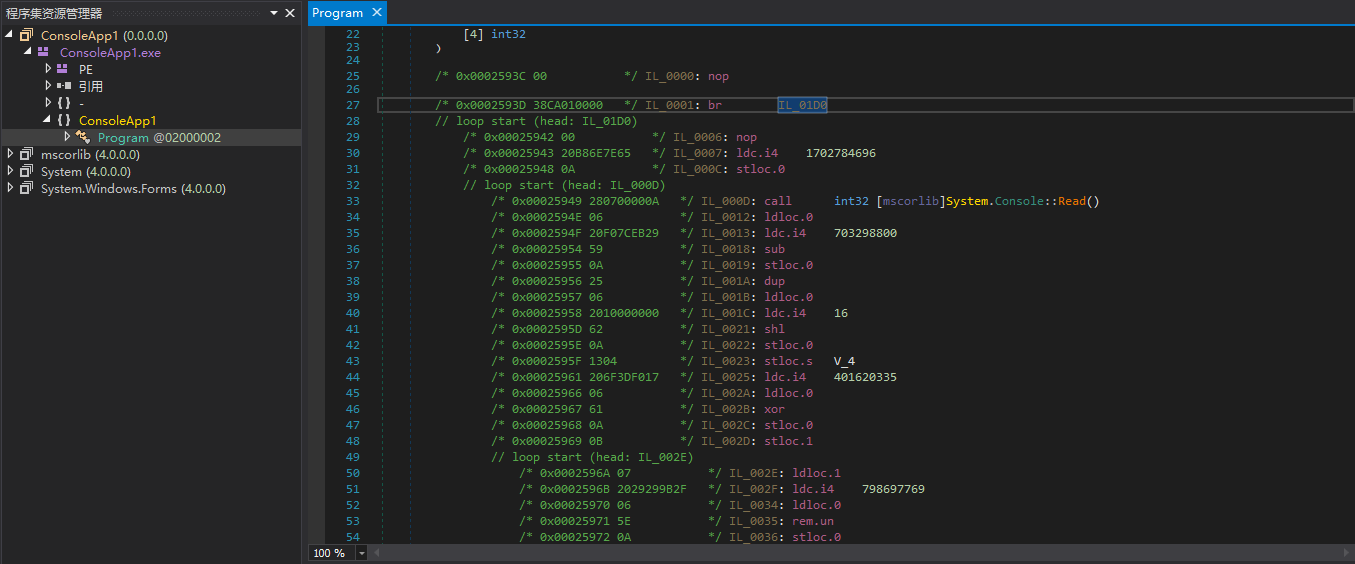
我们要制订一个最简单的方案来清理掉Mutation,所以把dnSpy反编译模式切换回IL,观察num更新的语句究竟是什么样的。
这个方法的入口点就是一个br跳转,所以直接看br跳转到的基本块是怎么样的。
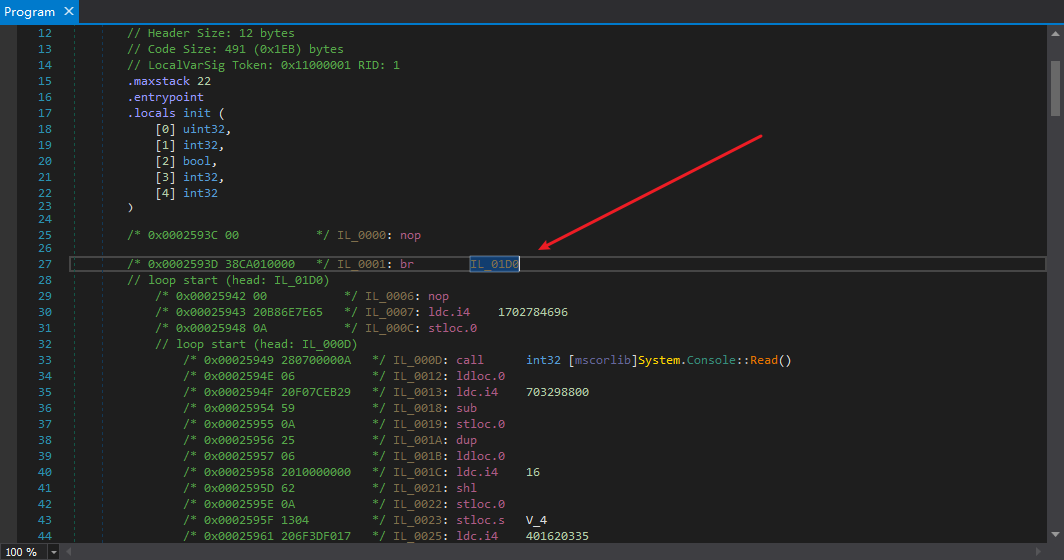
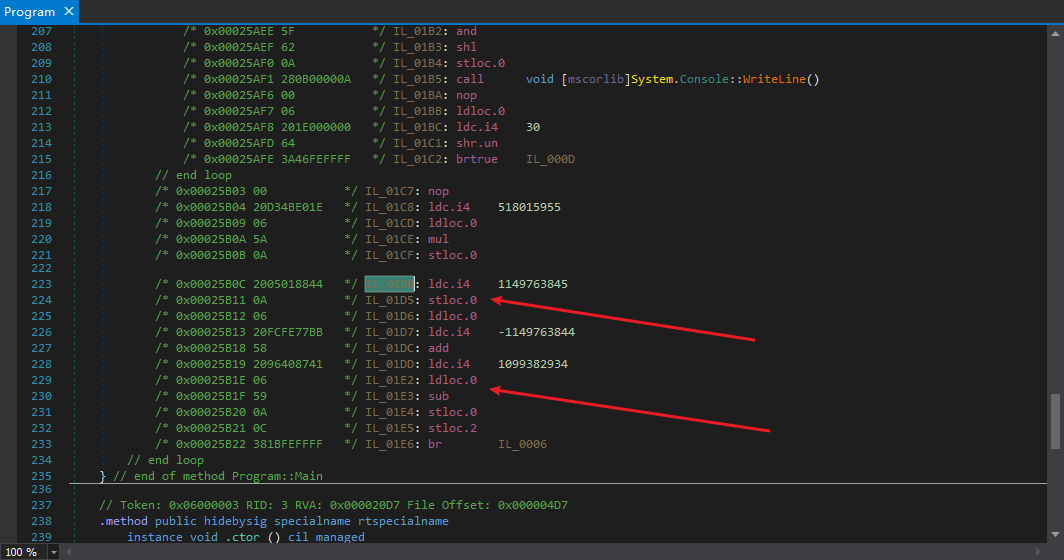
由于这个基本块是整个方法的入口点,那么这个基本块也一定是Mutation初始化的地方,也会是我们使用模拟器模拟的入口点,具体的可以看我以前的.NET控制流分析(二)-反混淆,搜一下搜得到,先看看里面清理ConfuserEx的switch混淆和清理VMProtect.NET的Mutation很相似。
第一个箭头指着的
1
2
| ldc.i4 1149763845
stloc.0
|
就是上下文num的初始化,后面会使用类似如下的代码来更新num
1
2
3
4
| ldc.i4 1099382934
ldloc.0
sub
stloc.0
|
如果代码中还有常量,常量的解密和这个也是相似的,因为写之前已经分析过了,所以就不再写一遍了。
反混淆
这类混淆虽然简单,但是实际清理起来有些麻烦,为什么这么说?因为你要模拟整个控制流,模拟每一种可能的分支情况,才能确保你的解密结果是万无一失的。要模拟就非常麻烦了,可能造成死循环。模拟时,解密得到的结果如何处理,又是一个问题。
尝试
以下内容均为我的尝试(只是部分),我也是在各种尝试之后找到的解决方案。
我最开始的想法是特征匹配
1
2
3
| ldc.i4
ldloc
add/sub/mul/div ...
|
这样的代码,遇到了直接替换成
最后失败了,效果不太好,因为有些地方的特征并不是这样,比如混淆分支跳转指令前的(说是混淆分支跳转,因为这个跳转结果是确定的,每次跳转结果都一样)
所以我想出了个非常投机取巧的方法,只替换
为
这样可以适用于所有情况。
我在每次模拟后,判断模拟的指令是不是读取变量num的,如果是,我直接替换为
但是发现这样有个很大的问题。因为我没办法准确地识别被VMProtect.NET Mutation混淆的方法。肉眼看C#反编译结果确实一眼看出,但是用代码如何识别是一个非常大的难题。有的时候判断有误,把没混淆的识别为混淆了,然后模拟出结果,直接替换,最后发现不该替换,这下就很麻烦了。解密后原地替换,还有其它的问题,总之非常不好。
最后我决定使用一个集合来保存解密结果,同时可以验证每一次模拟的结果是不是相同的,如果不同那说明代码有问题,或者VMProtect有BUG,能增强稳定性。
写好逻辑
事实上最开始我是把逻辑和具体实现写在一起了,因为这样修改起来很方便,到后期基本上稳定,BUG没几个的时候,我才抽象出了逻辑,把底层的解密操作分开了。
因为我是写好了工具的,所以按我的源代码来讲解,先说抽象类。
以下是我的抽象类的成员列表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
| namespace ControlFlow.Deobfuscation {
public abstract class ConstantFlowDeobfuscatorBase {
protected readonly MethodBlock _methodBlock;
protected readonly Emulator _emulator;
protected Local _flowContext;
protected int _decryptedCount;
#if DEBUG
protected int _indent;
public bool DEBUG;
#endif
protected ConstantFlowDeobfuscatorBase(MethodBlock methodBlock);
protected virtual void Deobfuscate();
protected virtual void VisitAllBasicBlocks(BasicBlock basicBlock);
protected abstract void OnBegin();
protected abstract void OnEnd();
protected abstract IEnumerable<BasicBlock> GetEntries();
protected abstract void OnEmulateBegin(BasicBlock basicBlock, int index);
protected abstract void OnEmulateEnd(BasicBlock basicBlock, int index);
protected virtual void OnEmulateBegin(BasicBlock basicBlock);
protected virtual void OnEmulateEnd(BasicBlock basicBlock);
protected virtual BasicBlock EmulateBranch(BasicBlock basicBlock);
protected virtual void CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional(BasicBlock basicBlock);
#if DEBUG
private static string DEBUG_ToString(BasicBlock basicBlock);
#endif
protected abstract class BlockInfoBase {
public bool[] EmulationMarks;
public List<BasicBlock> NextBasicBlocks;
public bool IsEntered;
protected BlockInfoBase(BasicBlock basicBlock);
}
}
}
|
如果看过我原来的ConfuserEx的switch混淆的清理文章,可以发现这个和那个switch清理的抽象类很像,都是需要提供所有可用入口点,模拟到结束,从而覆盖整个方法,达到解密效果。
最关键的逻辑还是在VisitAllBasicBlocks这里,就这个方法,我改过N次,N次bug都是这里逻辑问题导致的。
所以我不贴有bug的代码了,直接贴现在正常工作的代码,里面有因为bug让我写的注释。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| protected virtual void VisitAllBasicBlocks(BasicBlock basicBlock) {
BlockInfoBase blockInfo;
blockInfo = basicBlock.PeekExtraData<BlockInfoBase>();
if (blockInfo.IsEntered)
return;
#if DEBUG
if (DEBUG)
Console.WriteLine($"{new string(' ', _indent)}{DEBUG_ToString(basicBlock)}: {_emulator.Locals[_flowContext]}");
#endif
blockInfo.IsEntered = true;
OnEmulateBegin(basicBlock);
for (int i = 0; i < basicBlock.Instructions.Count; i++)
if (blockInfo.EmulationMarks[i]) {
OnEmulateBegin(basicBlock, i);
if (!_emulator.Emulate(basicBlock.Instructions[i]))
throw new NotImplementedException("暂未实现模拟失败处理,需要更新反混淆模型,或者检查是否模拟了不需要模拟的指令");
OnEmulateEnd(basicBlock, i);
}
OnEmulateEnd(basicBlock);
switch (basicBlock.BranchOpcode.FlowControl) {
case FlowControl.Return:
case FlowControl.Throw:
break;
default:
BasicBlock nextBasicBlock;
nextBasicBlock = EmulateBranch(basicBlock);
if (nextBasicBlock is null) {
#if DEBUG
_indent += 2;
if (DEBUG)
Console.WriteLine(new string(' ', _indent) + "conditional");
#endif
CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional(basicBlock);
#if DEBUG
_indent -= 2;
#endif
}
else {
if (!blockInfo.NextBasicBlocks.Contains(nextBasicBlock))
blockInfo.NextBasicBlocks.Add(nextBasicBlock);
VisitAllBasicBlocks(nextBasicBlock);
}
break;
}
blockInfo.IsEntered = false;
}
|
这里的blockInfo.IsEntered原来是IsVisited,被我改成了IsEntered。为了防止模拟进入死循环,必须要防止一个基本块重复执行,但是这个度需要把握好。最开始打算如果已经模拟过这个基本块,那么就不模拟了。显然这个想法有问题。就比如文中的样本,在不同的分支下,都会跳转到那个Console.WriteLine的基本块,如果使用IsVisited来表示基本块只能模拟一次,那么就会出现不能模拟每一种分支情况,有可能导致误判。
为什么说可能误判,比如这个
1
2
3
4
| uint num = 0;
if (xxx)
num = RandomUInt32();
Console.WriteLine(num);
|
假设逻辑是一个基本块只能执行一次,我们先模拟的情况是if语句不执行,那么执行到
的时候,num的值是确定的,为0
然后我们模拟if分支执行的情况,因为Console.WriteLine的基本块是执行过的,所以我们不执行了。
那么最后,我们得到了一个解密结果,Console.WriteLine用的num的值是0,但是事实不是这样。
所以我们应该使用IsEntered来表示,如果已经处于一个基本块中,那么我们不能重复模拟这个基本块,来防止while(true)之类的死循环。在模拟一个基本块之前将基本块的IsEntered设置为true,在模拟完这个基本块的分支指令之后,设置为false,可以完美解决问题。
CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional的代码和ConfuserEx的switch混淆清理的代码一样(之前那个帖子的CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional的代码有bug,仔细对比下我等下发的,就知道为什么了,注意我的EmulationContext是引用类型)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| protected virtual void CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional(BasicBlock basicBlock) {
EmulationContext context;
context = _emulator.Context.Clone();
if (!(basicBlock.FallThrough is null)) {
VisitAllBasicBlocks(basicBlock.FallThrough);
_emulator.Context = context.Clone();
}
if (!(basicBlock.ConditionalTarget is null)) {
VisitAllBasicBlocks(basicBlock.ConditionalTarget);
_emulator.Context = context.Clone();
}
if (!(basicBlock.SwitchTargets is null))
foreach (BasicBlock target in basicBlock.SwitchTargets) {
VisitAllBasicBlocks(target);
_emulator.Context = context.Clone();
}
}
|
接下来是实现所有抽象方法和部分虚方法。代码直接贴出来了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
| namespace ControlFlow.Deobfuscation.Specials.VMProtect {
public sealed class MutationDeobfuscator : ConstantFlowDeobfuscatorBase {
private static readonly Code[] InitializeFlowContextCodes = new Code[] { Code.Ldc_I4, Code.Stloc };
private static readonly Code[] CanBeEmulatedCodes = new Code[] {
Code.Add, Code.Add_Ovf, Code.Add_Ovf_Un, Code.And, Code.Div, Code.Div_Un, Code.Mul, Code.Mul_Ovf, Code.Mul_Ovf_Un, Code.Neg, Code.Not, Code.Or, Code.Rem, Code.Rem_Un, Code.Shl, Code.Shr, Code.Shr_Un, Code.Sub, Code.Sub_Ovf, Code.Sub_Ovf_Un, Code.Xor,
Code.Ceq, Code.Cgt, Code.Cgt_Un, Code.Clt, Code.Clt_Un,
Code.Ldc_I4,
Code.Ldloc, Code.Stloc,
Code.Beq, Code.Bge, Code.Bge_Un, Code.Bgt, Code.Bgt_Un, Code.Ble, Code.Ble_Un, Code.Blt, Code.Blt_Un, Code.Bne_Un, Code.Br, Code.Brfalse, Code.Brtrue, Code.Endfilter, Code.Endfinally, Code.Leave, Code.Ret, Code.Rethrow, Code.Switch, Code.Throw
};
private List<BasicBlock> _basicBlocks;
private List<BasicBlock> _entries;
private bool _isNotMutation;
private MutationDeobfuscator(MethodBlock methodBlock) : base(methodBlock) {
}
public static int Deobfuscate(MethodBlock methodBlock) {
MutationDeobfuscator deobfuscator;
deobfuscator = new MutationDeobfuscator(methodBlock);
deobfuscator.Deobfuscate();
if (deobfuscator._decryptedCount > 0) {
NopRemover.Remove(methodBlock);
ConstantArithmeticRemover.Remove(methodBlock);
}
return deobfuscator._decryptedCount;
}
protected override void OnBegin() {
Dictionary<Local, int> frequencies;
int maxFrequency;
Local flowContext;
frequencies = new Dictionary<Local, int>();
_basicBlocks = _methodBlock.GetAllBasicBlocks();
foreach (BasicBlock basicBlock in _basicBlocks)
foreach (Instruction instruction in basicBlock.Instructions) {
Local local;
if (instruction.OpCode.Code != Code.Ldloc && instruction.OpCode.Code != Code.Stloc)
continue;
local = (Local)instruction.Operand;
if (!frequencies.ContainsKey(local))
frequencies[local] = 1;
else
frequencies[local]++;
}
maxFrequency = 0;
flowContext = null;
foreach (KeyValuePair<Local, int> frequency in frequencies)
if (frequency.Value > maxFrequency) {
maxFrequency = frequency.Value;
flowContext = frequency.Key;
}
if (!(flowContext is null) && (flowContext.Type.ElementType != ElementType.U4 ))
flowContext = null;
if (flowContext is null)
return;
_flowContext = flowContext;
_entries = new List<BasicBlock>();
foreach (BasicBlock basicBlock in _basicBlocks)
if (MayBeEntry(basicBlock, flowContext))
_entries.Add(basicBlock);
foreach (BasicBlock basicBlock in _basicBlocks)
basicBlock.PushExtraData(new BlockInfo(basicBlock));
_emulator.Interceptor = Interceptor;
}
private static bool MayBeEntry(BasicBlock basicBlock, Local flowContext) {
int index;
index = basicBlock.Instructions.IndexOf(InitializeFlowContextCodes);
if (index == -1)
return false;
if (basicBlock.Instructions[index + 1].Operand != flowContext)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
if (basicBlock.Instructions[i].Operand == flowContext)
return false;
return true;
}
private bool Interceptor(Emulator emulator, Instruction instruction) {
if (!CanBeEmulatedCodes.Contains(instruction.OpCode.Code)) {
emulator.UpdateStack(instruction);
return true;
}
if (instruction.Operand is Local && instruction.Operand != _flowContext) {
emulator.UpdateStack(instruction);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected override void OnEnd() {
if (_isNotMutation)
_decryptedCount = 0;
foreach (BasicBlock basicBlock in _basicBlocks) {
if (_decryptedCount != 0) {
List<BasicBlock> nextBasicBlocks;
foreach (KeyValuePair<int, List<int>> decryptedValue in basicBlock.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().DecryptedValues) {
if (decryptedValue.Value.Count != 1)
continue;
basicBlock.Instructions[decryptedValue.Key] = OpCodes.Ldc_I4.ToInstruction(decryptedValue.Value[0]);
}
nextBasicBlocks = basicBlock.PeekExtraData<BlockInfoBase>().NextBasicBlocks;
if (nextBasicBlocks.Count == 1)
switch (basicBlock.BranchOpcode.StackBehaviourPop) {
case StackBehaviour.Popi:
basicBlock.Instructions.Add(OpCodes.Pop.ToInstruction());
basicBlock.SetBr(nextBasicBlocks[0]);
break;
case StackBehaviour.Pop1_pop1:
basicBlock.Instructions.Add(OpCodes.Pop.ToInstruction());
basicBlock.Instructions.Add(OpCodes.Pop.ToInstruction());
basicBlock.SetBr(nextBasicBlocks[0]);
break;
}
#if DEBUG
if (nextBasicBlocks.Count > 1) {
System.Console.WriteLine(BlockPrinter.ToString(_methodBlock));
System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert(false, "存在不同的分支模拟结果");
}
#endif
}
basicBlock.PopExtraData();
}
}
protected override IEnumerable<BasicBlock> GetEntries() {
return _entries;
}
protected override void OnEmulateBegin(BasicBlock basicBlock, int index) {
}
protected override void OnEmulateEnd(BasicBlock basicBlock, int index) {
List<Instruction> instructions;
if (_isNotMutation)
return;
instructions = basicBlock.Instructions;
if (instructions[index].OpCode.Code == Code.Ldloc && instructions[index].Operand == _flowContext) {
Int32Value value;
Dictionary<int, List<int>> decryptedValues;
List<int> existingValues;
value = _emulator.EvaluationStack.Peek() as Int32Value;
if (value is null) {
_isNotMutation = true;
return;
}
decryptedValues = basicBlock.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().DecryptedValues;
if (!decryptedValues.TryGetValue(index, out existingValues)) {
existingValues = new List<int>();
decryptedValues.Add(index, existingValues);
}
if (!existingValues.Contains(value.Signed)) {
existingValues.Add(value.Signed);
_decryptedCount++;
}
if (existingValues.Count > 1) {
_decryptedCount--;
_isNotMutation = true;
#if DEBUG
System.Console.WriteLine(BlockPrinter.ToString(_methodBlock));
System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert(false, "存在不同的解密结果");
#endif
}
}
}
protected override void VisitAllBasicBlocks(BasicBlock basicBlock) {
if (_isNotMutation)
return;
base.VisitAllBasicBlocks(basicBlock);
}
protected override void CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional(BasicBlock basicBlock) {
if (_isNotMutation)
return;
base.CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional(basicBlock);
}
private sealed class BlockInfo : BlockInfoBase {
private readonly Dictionary<int, List<int>> _decryptedValues;
public Dictionary<int, List<int>> DecryptedValues => _decryptedValues;
public BlockInfo(BasicBlock basicBlock) : base(basicBlock) {
_decryptedValues = new Dictionary<int, List<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < EmulationMarks.Length; i++)
EmulationMarks[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
|
首先我们要找出哪个局部变量是Mutation的上下文,但实际上我只能大概的判断是不是,这个不模拟一遍确实很难确定。这个我们写在OnBegin里面,因为这是初始化步骤。具体的实现在上面有。
OnBegin的最后一行有个
1
| _emulator.Interceptor = Interceptor;
|
这个Interceptor是我新加入的,之前放出的模拟器源码里面没这个。这个东西相当于Hook。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public delegate bool Interceptor(Emulator emulator, Instruction instruction);
|
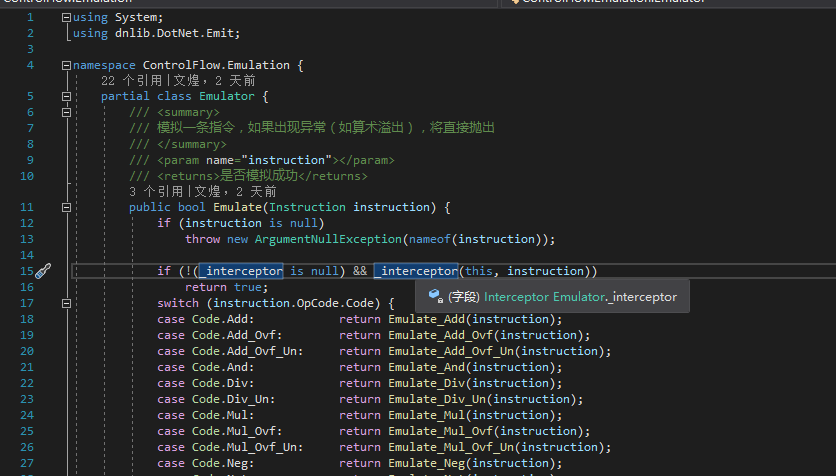
如果你们要用的话拿我之前放出的源码改改就行。
回到反混淆器里面实现的Interceptor。为了提高稳定性,不模拟无关代码,也为了提高速度,我过滤了很多指令,因为VMProtect.NET的Mutation只需要运算指令,比较指令,取值指令,分支指令这4类。
对于ldloc,也就是读取变量的指令,还要特殊处理一次,防止读取到无关Mutation的变量的值,防止模拟器计算不该计算的,导致分支模拟出现问题。
VMProtect.NET的Mutation会加密常量,还会添加混淆分支的代码,所以我们要在模拟结束的之后,全部还原。这部分在OnEnd中实现。
总的来说VMProtect.NET的Mutation一般般,不能被C#反编译结果吓到,因为那是故意唬你的,试都不试怎么知道到底能不能脱呢?
至于VMProtect.NET的Virtualization模式我还没搞定,不知道在研究反虚拟化的大佬愿不愿意分享一下经验,我对这块一直不太清楚,打算研究研究。
工具下载
DeMutation.zip
目前工具很稳定,测试了很多次,无BUG,偶尔会提示无效分支指令,那个不用管,对程序运行完全无影响。
清理前后对比
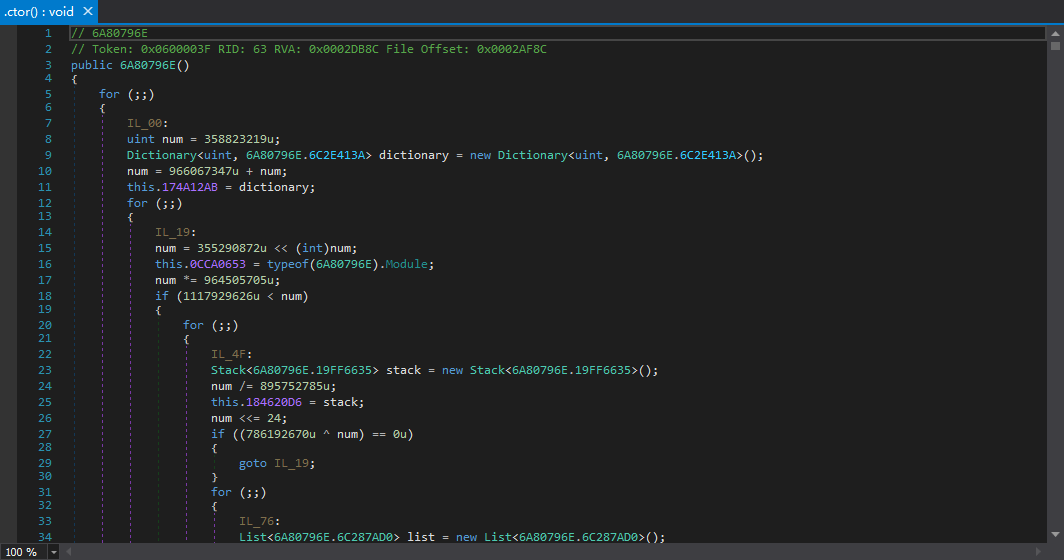
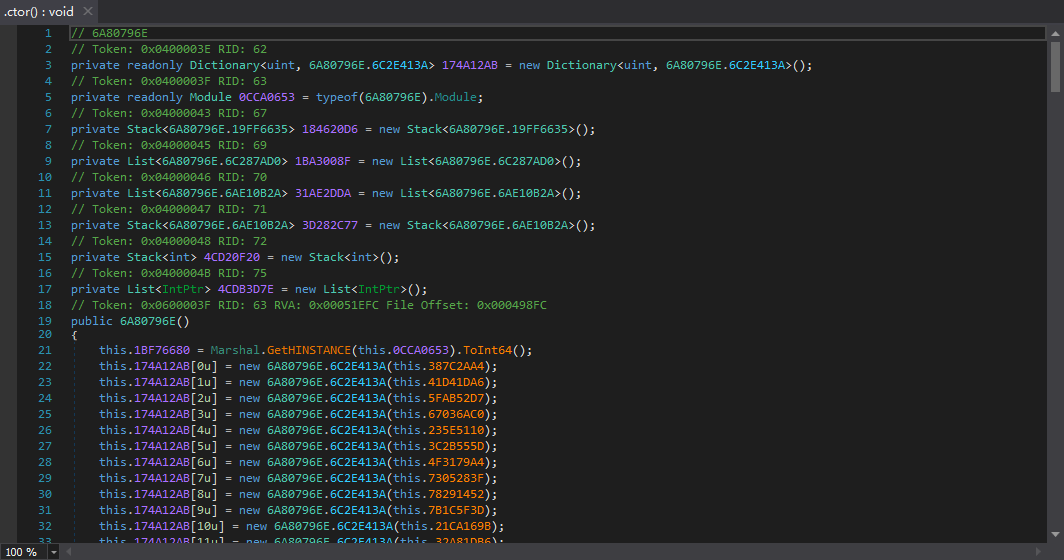
效果还是很不错的











