在了解基本的控制流知识后,本文会继续基于此介绍一些还原控制流混淆的手段,并以ConfuserEx的控制流混淆为例写出一个还原它的脱壳机。
前言 本来想分成2块写的,因为有一部分简单,还有一部分很难,非常难。但是想想还是算了,一篇文章写完也可以,因为都是和反混淆有关的内容。不过估计文章会非常长,字数非常多。
这篇文章还是要按顺序看,文章前半部分讲的是简单的,后半部分是难的,并且需要前半部分的一些知识。
前半部分比较简单,会说一些比较通用的代码和思路。
后半部分更有征对性,实战讲解ConfuserEx的控制流混淆清除。为什么讲ConfuserEx的控制流混淆?因为我觉得ConfuserEx的控制流混淆是最难的,至少在我遇到的壳里面来说。其它壳都是一个简单的switch(num),case里面一条num=x;就没了,而ConfuserEx的控制流混淆是线性的,下一个被执行的基本块与上一个被执行的基本块有关,无法静态解密switch混淆,必需虚拟执行。
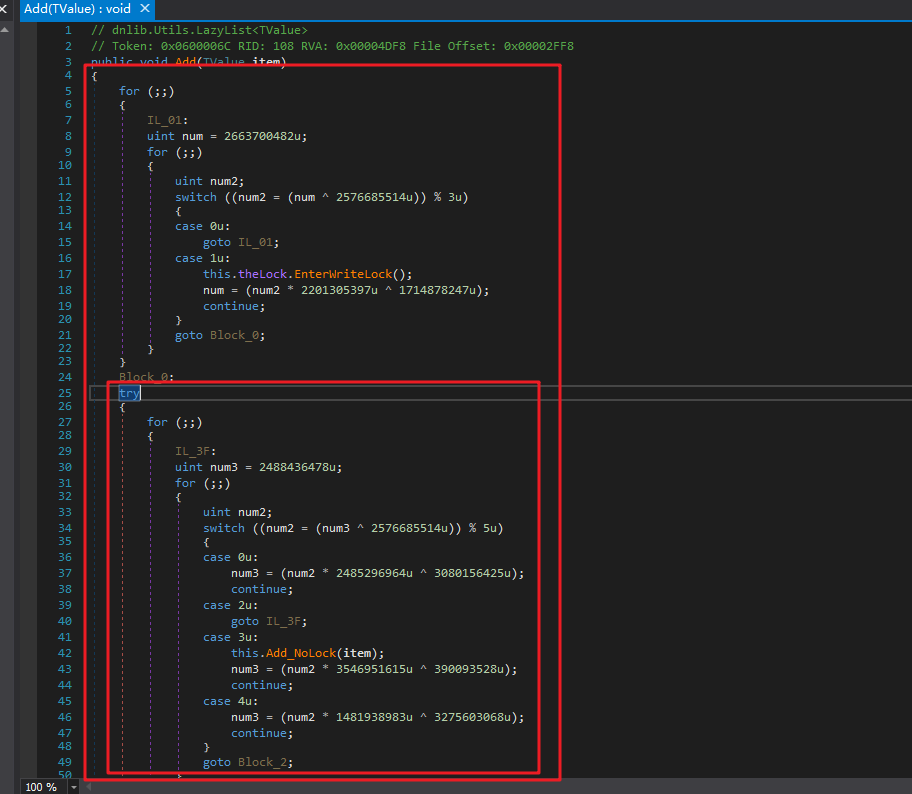
基础 递归模型 很多时候一个方法里面会有try块,这样的话,一个方法块里面就会有小作用域,也就是那个try块。控制流混淆只会在同一个作用域里面进行混淆,没见过会跨作用域混淆的。什么意思的?
比如这个大的红框,就是一个作用域,try包括的地方可以看作一个整体,控制流混淆的时候不会把try这个整体拆成多个部分。而try内部是一个作用域,不是一个整体,可以拆成多个部分,继续混淆。
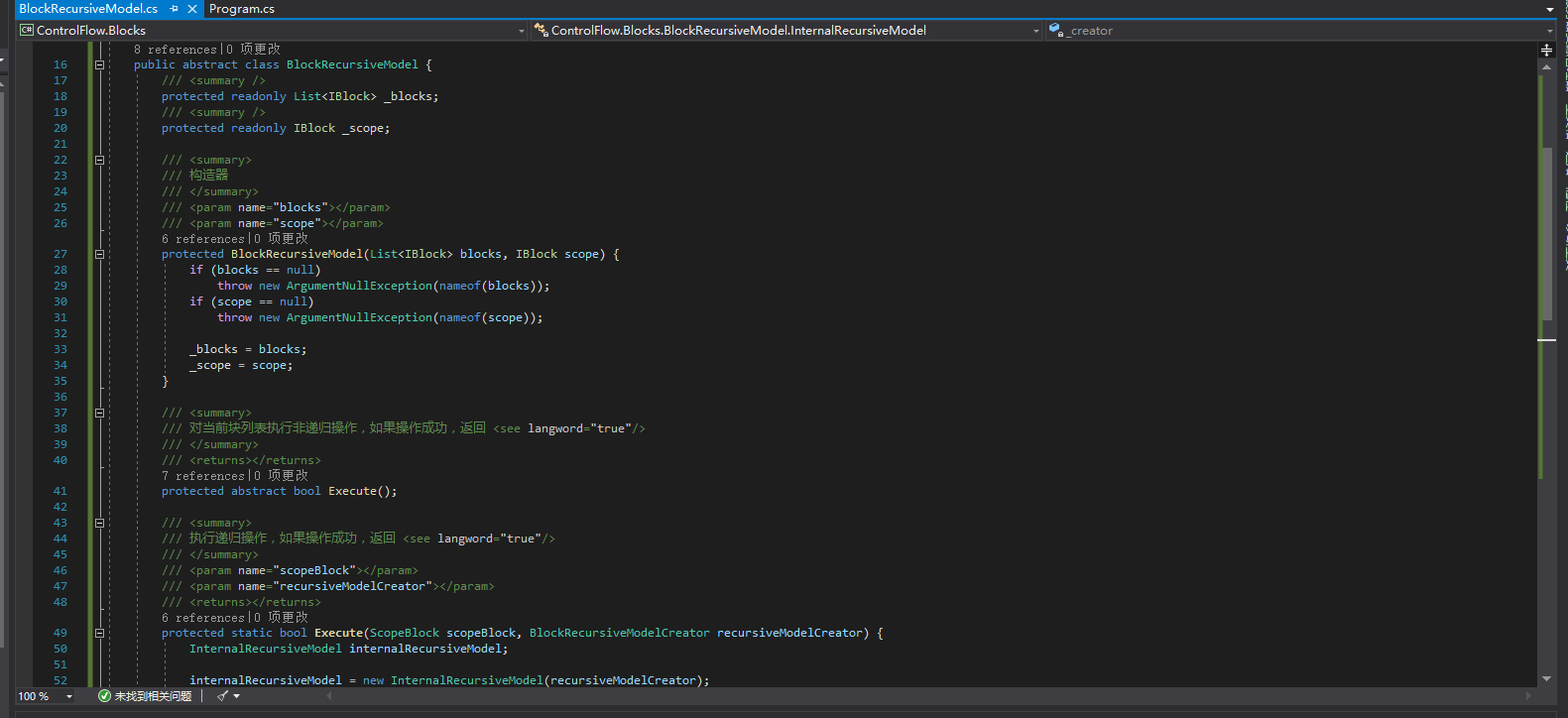
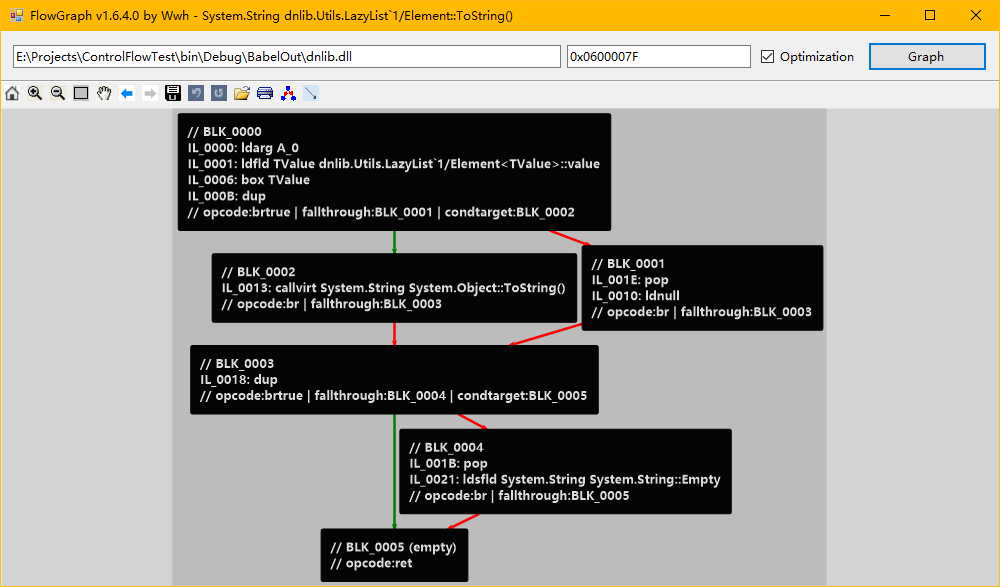
所以我们要写出Helper类能简化遍历每一个作用域来反混淆的操作。这个类就叫做BlockRecursiveModel,代码在这个系列的上一篇文章的附件里有。这里就截图看看大概样子。
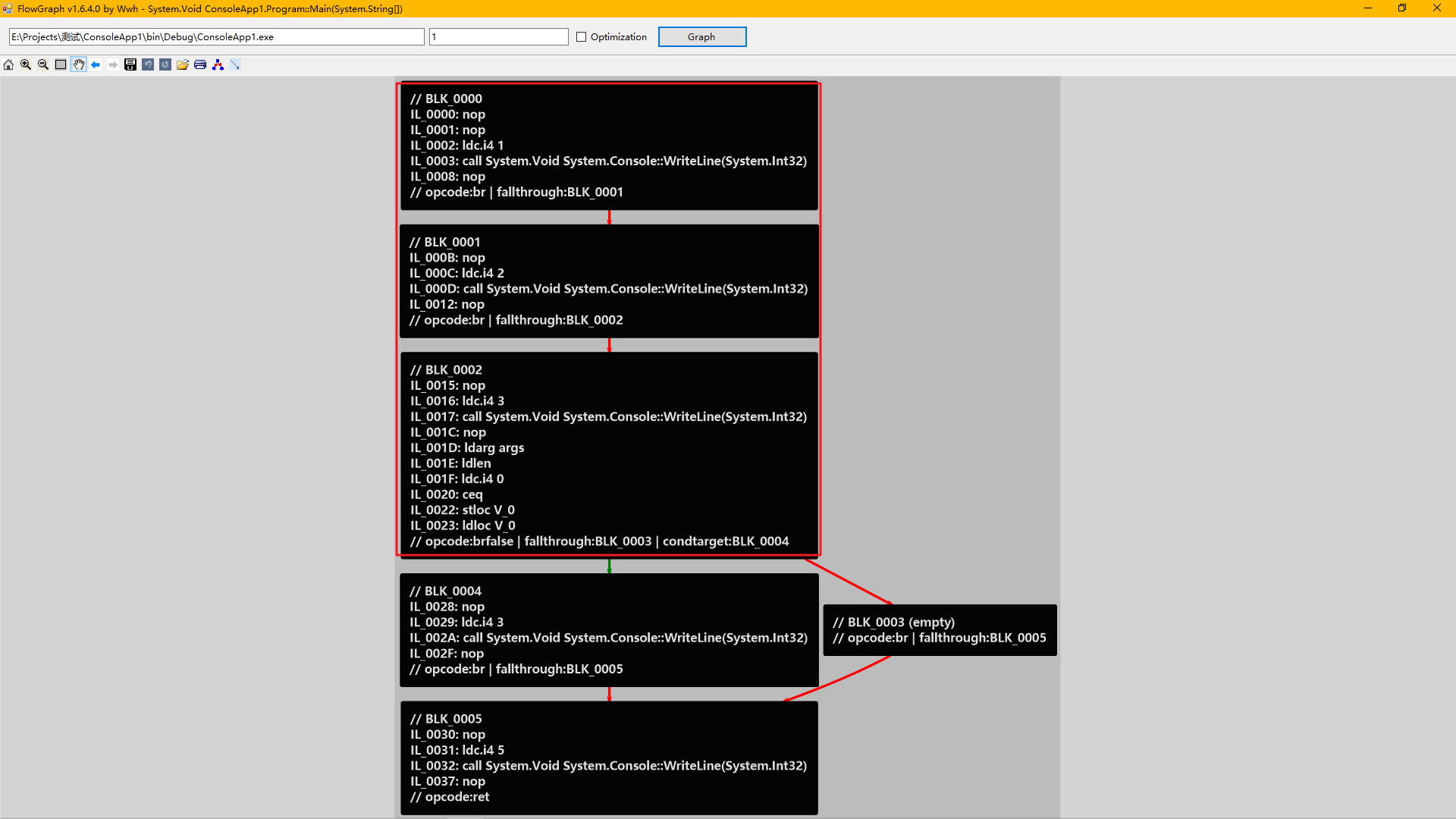
块排序器 为什么要排序?首先是减小代码体积,如果不排序,IL代码可能就会像这样,到处是无条件跳转指令br,让我们几乎无法阅读IL代码。
而排序之后逻辑清晰很多:
这只是一个非常简单的方法体。如果是复杂的方法体,代码会膨胀很多,排序显得非常重要。
当然,排序只是对生成的指令流有影响,对我们分析树状结构的控制流,也就是分成块之后的控制流是没有影响的。
分块之后无论是什么顺序储存在List<T>里面,结构其实都是一样的:
这个是我写的工具,文章末尾会附上编译好的程序。
有了刚才说的BlockRecursiveModel,块排序的代码其实非常简单,我们要先分析出在相同作用域内,块与块直接的引用关系,再使用DFS排序就行了。
要分析引用关系,我们还是要先定义个额外信息,来储存我们分析的结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private sealed class BlockInfo { private readonly List<IBlock> _references; private bool _isVisited; public List<IBlock> References => _references; public bool IsVisited { get => _isVisited; set => _isVisited = value ; } }
References表示的是引用,意思是会跳转到哪些块。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 private void AddXref (BasicBlock source, BasicBlock target ) IBlock targetRoot; List<IBlock> references; targetRoot = target.GetRootBlock(_scope); if (targetRoot == null ) return ; references = source.GetRootBlock(_scope).PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().References; if (!references.Contains(targetRoot)) references.Add(targetRoot); } public static IBlock GetRootBlock (this IBlock block, IBlock scope if (block == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (block)); if (scope == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (scope)); while (true ) { if (block.Scope == scope) return block; else block = block.Scope; if (block == null ) return null ; } }
代码里面的source代表会发生跳转的基本块,target表示会跳转到的基本块。
分析出所有引用关系之后,我们直接使用DFS排序就行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 private sealed class DfsSorter { private readonly List<IBlock> _blocks; private readonly Stack<IBlock> _blockStack; public DfsSorter (List<IBlock> blocks ) if (blocks == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (blocks)); _blocks = blocks; _blockStack = new Stack<IBlock>(_blocks.Count); } public Stack<IBlock> Sort () DfsSort(_blocks[0 ]); return _blockStack; } private void DfsSort (IBlock block ) BlockInfo blockInfo; blockInfo = block.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>(); blockInfo.IsVisited = true ; for (int i = blockInfo.References.Count - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (!blockInfo.References[i].PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().IsVisited) DfsSort(blockInfo.References[i]); _blockStack.Push(block); } }
整个排序的完整代码都在上一篇文章的附件的压缩包里面,叫BlockSorter.cs
移除NOP 移除NOP这个操作非常简单,因为我们已经转换成了块,遍历每个基本块块,把每个基本块的NOP都移除就好。
既然简单,那为什么还要提这个呢?
因为我们的目标是把所有情况尽可能的简化,变成一种情况,这样我们处理起来就方便很多。而NOP的存在可能会影响我们识别特征。
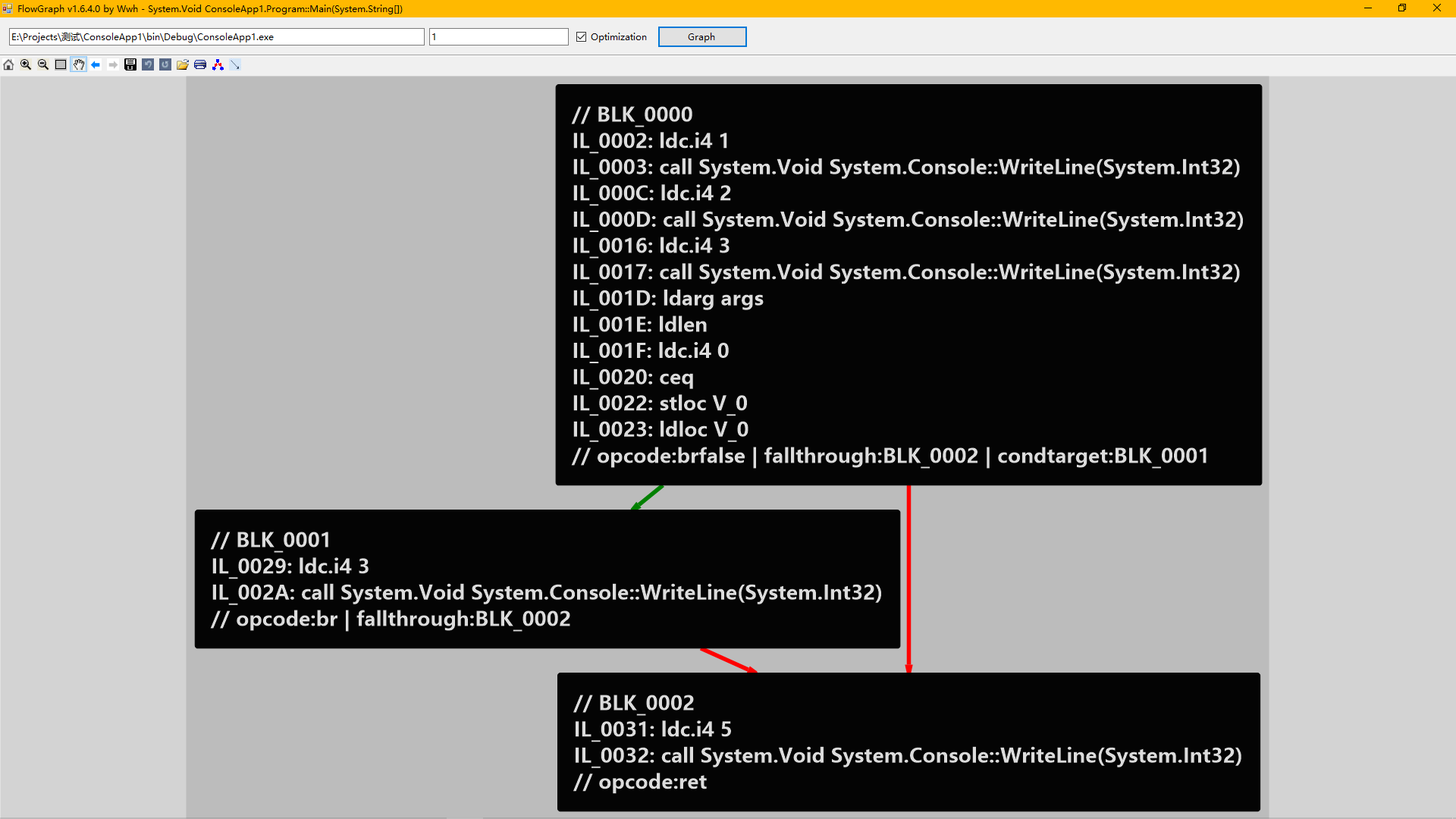
基本块内联 什么叫内联,比如这样:
红框中3个基本块就是可以内联到一起的,为什么呢?因为BLK_0002只被一个基本块引用了,BLK_0001也是,只被一个基本块引用,并且引用方是无条件跳转,那就可以内联起来。BLK_0004虽然只被一个基本块引用,但是引用方BLK_0002是条件跳转,我们就不能内联。
内联之后:
是不是效果明显,控制流清晰了很多,没有冗余的东西?
这里再扯一下我的FlowGraph,这个工具有个Optimization选项,开了之后就会把可以内联的块都内联到一起,并且清除NOP,对块进行排序。
除了这种情况,我们还有一种情况可以内联,就是某个基本块是空块,并且跳转指令是无条件跳转指令br。这种情况下,无论引用方有几个,引用方是什么跳转指令,我们都可以内联。
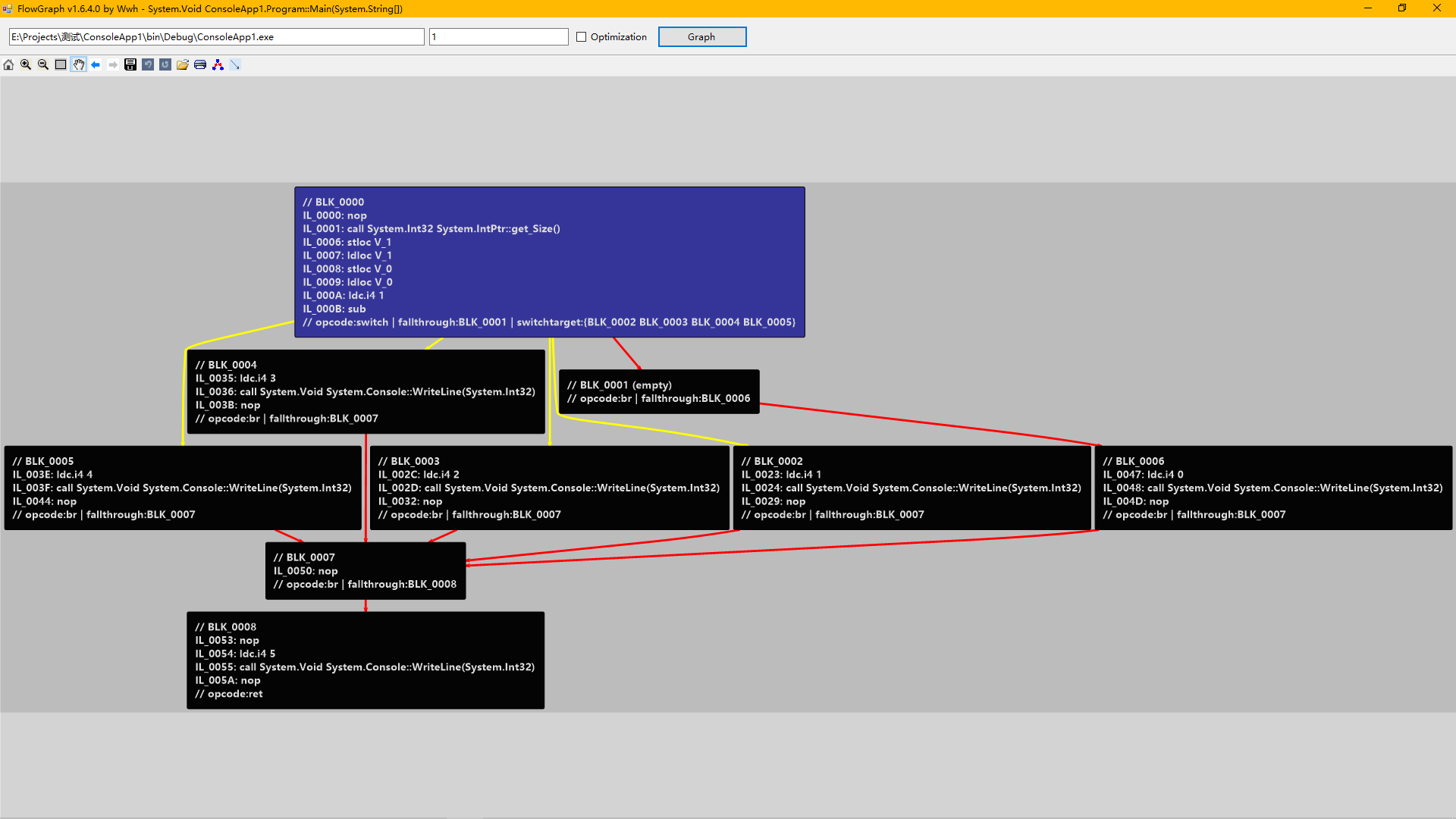
比如这样的:
这里的BLK_0007就是一个空块(nop指令等于不存在,我们会优化掉),而且是跳转指令是无条件跳转指令br。虽然BLK_0007的引用方有BLK_0002 BLK_0003 BLK_0004 BLK_0005 BLK_0006共5个,但是我们都可以内联起来。
内联起来的效果:
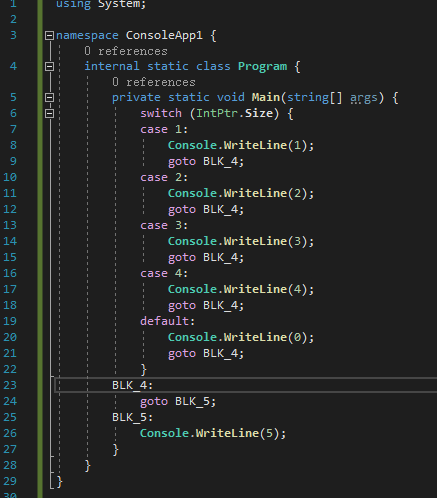
而这一段控制流的源代码其实非常简单,就是Debug模式下编译一个switch+goto
脑补一下,这个代码生成是不是更像我们开了优化之后的控制流图?
这个就是内联的牛逼之处,可以极大地简化控制流。虽然牛逼,但是实现就比上面地代码更复杂了。
实际上也没复杂多少,代码直接放出来,其实就200行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 using System.Collections.Generic;using ControlFlow.Blocks;using dnlib.DotNet.Emit;namespace ControlFlow.Deobfuscation { public sealed class BlockInliner : BlockRecursiveModel { private BlockInliner (List<IBlock> blocks, IBlock scope ) : base (blocks, scope ) } public static bool Inline (MethodBlock methodBlock ) bool result; methodBlock.PushExtraDataAllBasicBlocks(() => new BlockInfo()); new BlockXref(methodBlock, AddXref).Analyze(); result = Execute(methodBlock, (blocks, scope) => new BlockInliner(blocks, scope)); methodBlock.PopExtraDataAllBasicBlocks(); return result; } private static void AddXref (BasicBlock source, BasicBlock target ) List<BasicBlock> references; List<BasicBlock> dereferences; references = source.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().References; if (!references.Contains(target)) references.Add(target); dereferences = target.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().Dereferences; if (!dereferences.Contains(source)) dereferences.Add(source); } protected override bool Execute () bool isModified; bool next; if (_blocks.Count < 2 ) return false ; isModified = FixEntryBlockIfBrOnly(); do { for (int i = 1 ; i < _blocks.Count; i++) { BasicBlock target; BlockInfo targetInfo; target = _blocks[i] as BasicBlock; if (target == null ) continue ; targetInfo = target.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>(); if (CanInline(target, targetInfo)) { UpdateReferencesOfDereferences(target, targetInfo); UpdateDereferencesOfReferences(target, targetInfo); targetInfo.IsInlineed = true ; } } next = _blocks.RemoveAll(block => block is BasicBlock && block.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().IsInlineed) != 0 ; if (next) isModified = true ; } while (next); return isModified; } private static bool CanInline (BasicBlock target, BlockInfo targetInfo ) if (target.IsEmpty && target.BranchOpcode.Code == Code.Br) { return true ; } else { BasicBlock dereference; if (targetInfo.Dereferences.Count != 1 ) return false ; dereference = targetInfo.Dereferences[0 ]; if (dereference.BranchOpcode.Code != Code.Br) return false ; return true ; } } private static void UpdateReferencesOfDereferences (BasicBlock target, BlockInfo targetInfo ) foreach (BasicBlock dereference in targetInfo.Dereferences) { if (dereference.BranchOpcode.Code == Code.Br) { if (!target.IsEmpty) dereference.Instructions.AddRange(target.Instructions); dereference.BranchOpcode = target.BranchOpcode; dereference.FallThrough = target.FallThrough; dereference.ConditionalTarget = target.ConditionalTarget; dereference.SwitchTargets = target.SwitchTargets; } else { if (dereference.FallThrough == target) dereference.FallThrough = target.FallThrough; if (dereference.ConditionalTarget == target) dereference.ConditionalTarget = target.FallThrough; if (dereference.SwitchTargets != null ) for (int j = 0 ; j < dereference.SwitchTargets.Count; j++) if (dereference.SwitchTargets[j] == target) dereference.SwitchTargets[j] = target.FallThrough; } ListReplace(dereference.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().References, target, targetInfo.References); } } private static void UpdateDereferencesOfReferences (BasicBlock target, BlockInfo targetInfo ) foreach (BasicBlock reference in targetInfo.References) ListReplace(reference.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().Dereferences, target, targetInfo.Dereferences); } private static void ListReplace <T >(List<T> list, T oldItem, List<T> newItems ) if (newItems.Count > 1 ) { list.Remove(oldItem); foreach (T newItem in newItems) if (!list.Contains(newItem)) list.Add(newItem); } else if (newItems.Count == 1 ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < list.Count; i++) if (ReferenceEquals(list[i], oldItem)) list[i] = newItems[0 ]; } } private bool FixEntryBlockIfBrOnly () if (!IsBrOnlyBlock(_blocks[0 ])) return false ; BasicBlock entryBlock; IBlock fallThroughRoot; entryBlock = (BasicBlock)_blocks[0 ]; fallThroughRoot = GetNonBrOnlyFallThrough(entryBlock).GetRootBlock(_scope); _blocks[_blocks.IndexOf(fallThroughRoot)] = entryBlock; _blocks[0 ] = fallThroughRoot; return false ; } private static bool IsBrOnlyBlock (IBlock block ) BasicBlock basicBlock; basicBlock = block as BasicBlock; return basicBlock != null && IsBrOnlyBlock(basicBlock); } private static bool IsBrOnlyBlock (BasicBlock basicBlock ) return basicBlock.IsEmpty && basicBlock.BranchOpcode.Code == Code.Br; } private static BasicBlock GetNonBrOnlyFallThrough (BasicBlock basicBlock ) return IsBrOnlyBlock(basicBlock) ? GetNonBrOnlyFallThrough(basicBlock.FallThrough) : basicBlock; } private sealed class BlockInfo { private List<BasicBlock> _references; private List<BasicBlock> _dereferences; private bool _isInlineed; public List<BasicBlock> References { get => _references; set => _references = value ; } public List<BasicBlock> Dereferences { get => _dereferences; set => _dereferences = value ; } public bool IsInlineed { get => _isInlineed; set => _isInlineed = value ; } public BlockInfo () _references = new List<BasicBlock>(); _dereferences = new List<BasicBlock>(); } } } }
还是再强调一下,控制流分析系列的文章肯定不会简单,走马观花地看是不行的,要完全地看懂上面贴出的代码,还是要自己编译上面的代码(放到上一篇文章放出的源码里面编译),到VS里面单步调试,一点一点看完整的流程。
标准化 之前写的3个小节,都是标准化需要的操作。什么是标准化?把控制流化简到最简,就是标准化。对控制流进行标准化之后,我们匹配特征将会非常的容易,清理效果可以提升很多。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public static MethodBlock CreateStandardMethodBlock (this MethodDef methodDef if (methodDef == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (methodDef)); MethodBlock methodBlock; methodBlock = methodDef.CreateMethodBlock(); methodBlock.Standardize(); return methodBlock; } public static void Standardize (this MethodBlock methodBlock if (methodBlock == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (methodBlock)); NopRemover.Remove(methodBlock); BlockSorter.Sort(methodBlock); BlockInliner.Inline(methodBlock); BlockSorter.Sort(methodBlock); }
Switch混淆 我目前遇到的最难的控制流混淆应该就是ConfuserEx的Switch混淆,能搞定ConfuserEx的Switch混淆,其它控制流混淆应该没问题了,所以这里只讲ConfuserEx。编译好的工具文章末尾也有。
ConfuserEx的控制流混淆有很多种模式,这里只说ConfuserEx-GUI加出的控制流混淆,也就是Switch-Normal模式。其它模式可以看官方文档 Control Flow Protection - Wiki 。其它模式的反混淆,原理都差不多的,就不重复讲了。
然后关于ConfuserEx的一些Mod版本,控制流混淆的变化都不是特别大,反混淆原理也是相同的。
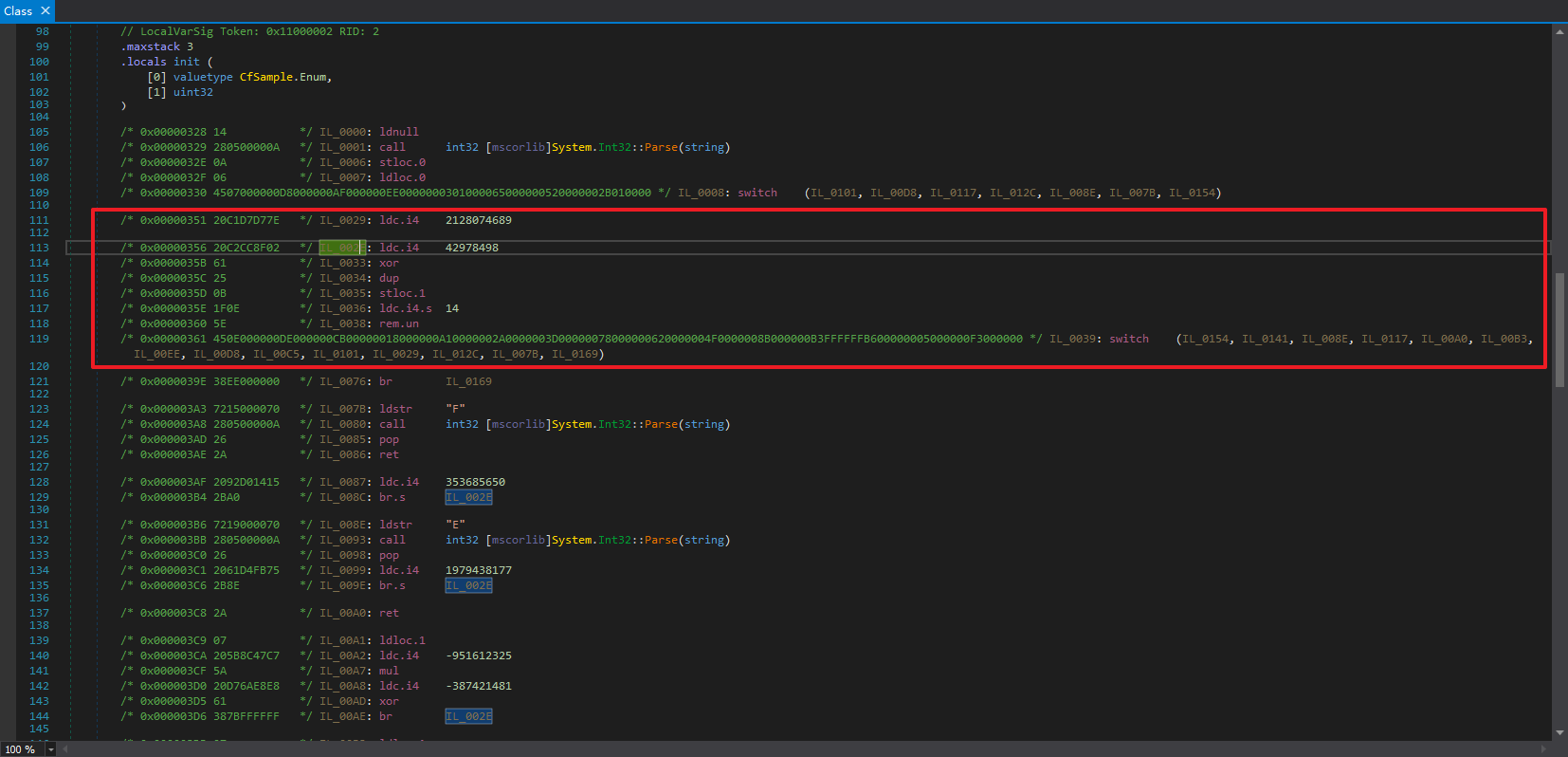
分析 找个ConfuserEx加控制流混淆的程序,用dnSpy先看看特征。
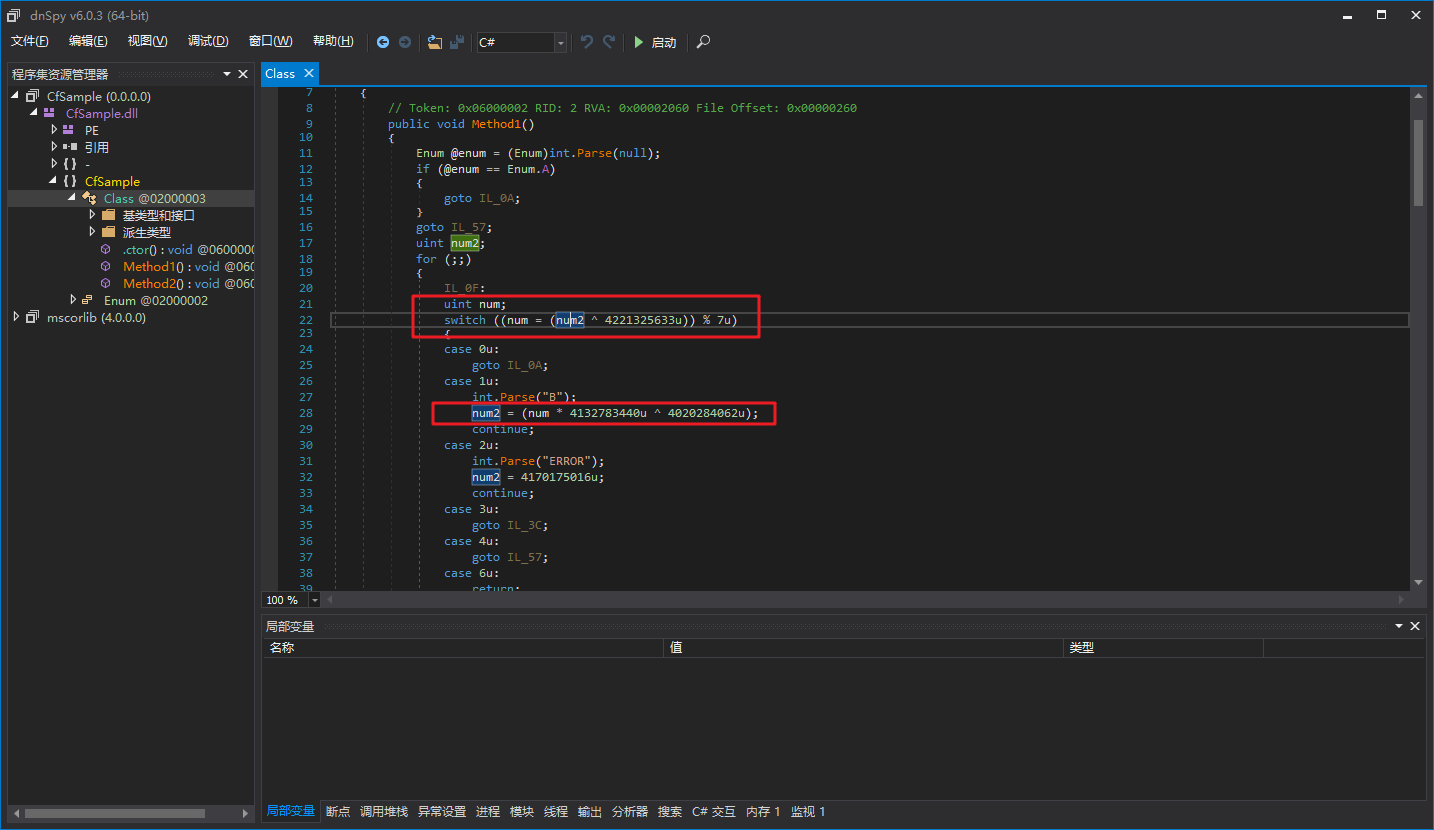
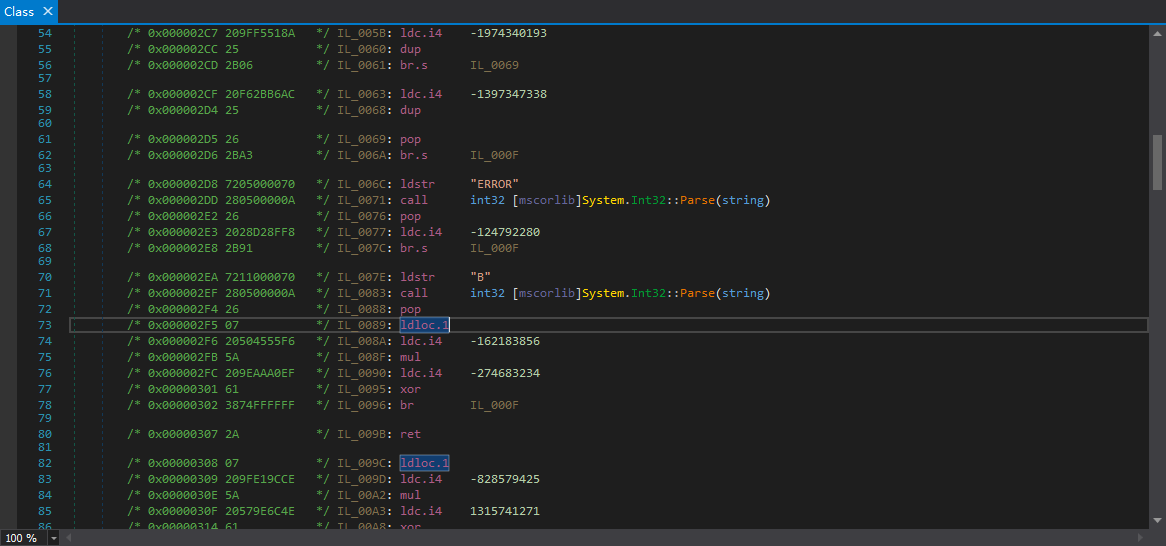
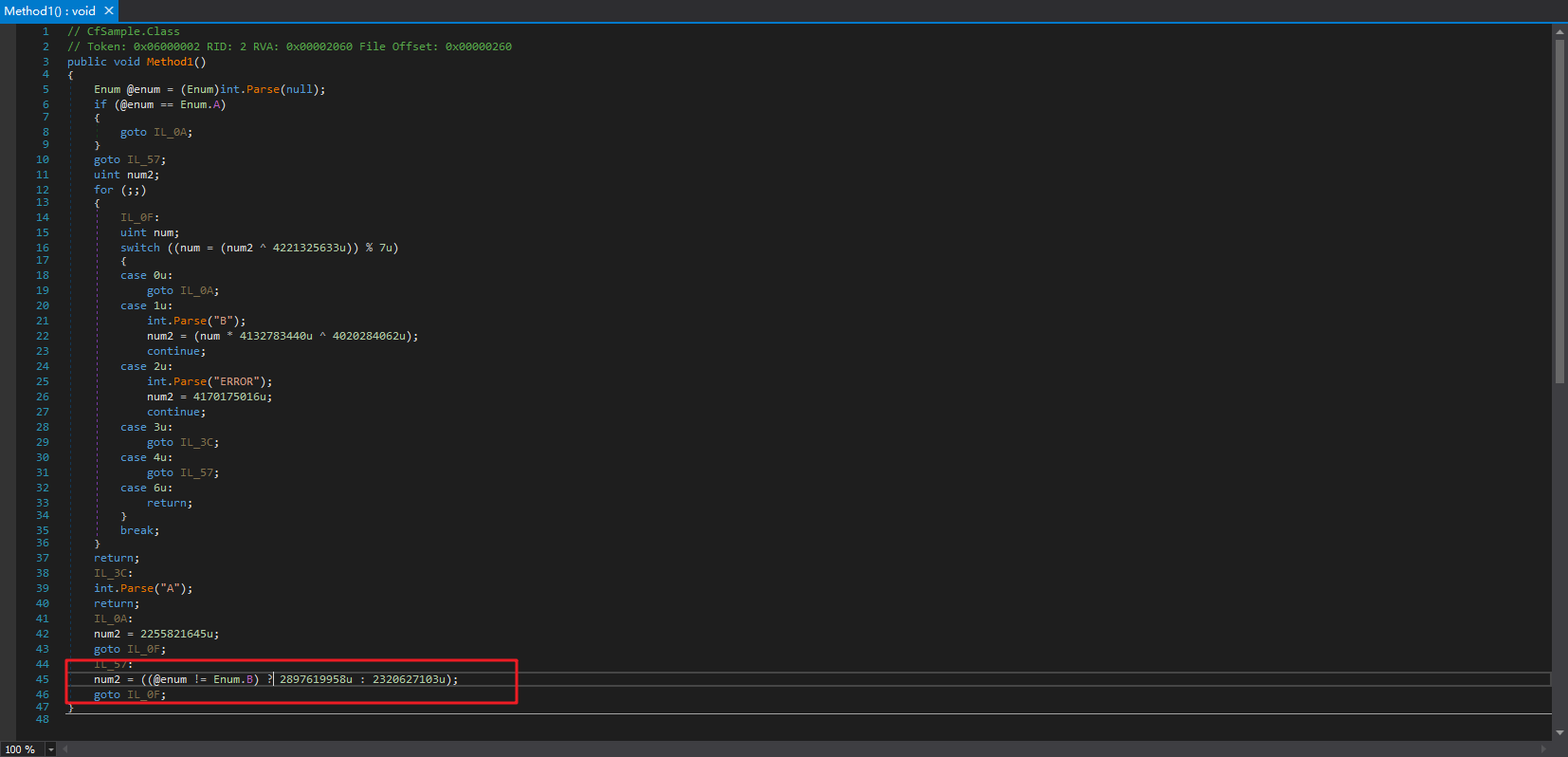
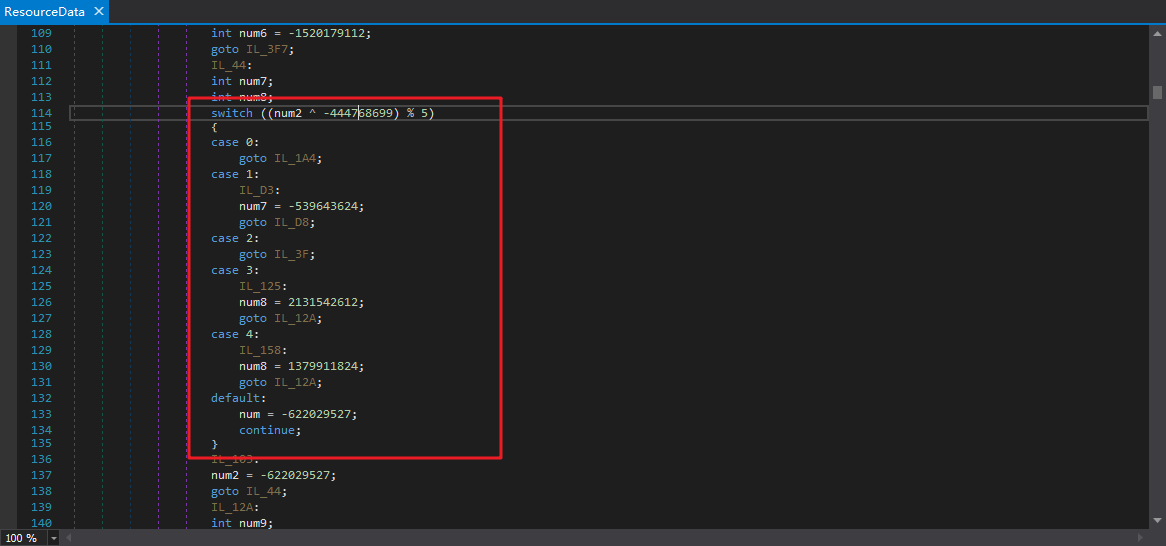
很明显的,这种不能静态解密,要跳转到的下一个case与上一个case有关。dnSpy看着有2个局部变量控制着控制流,事实上是这样吗?
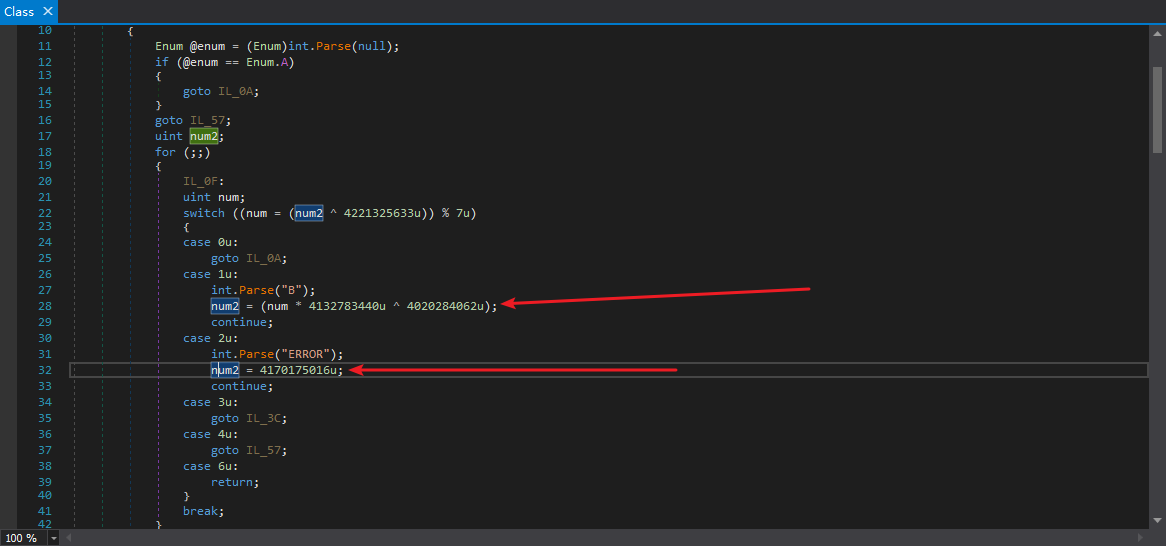
不是!其中有一个num是反编译器生成的。
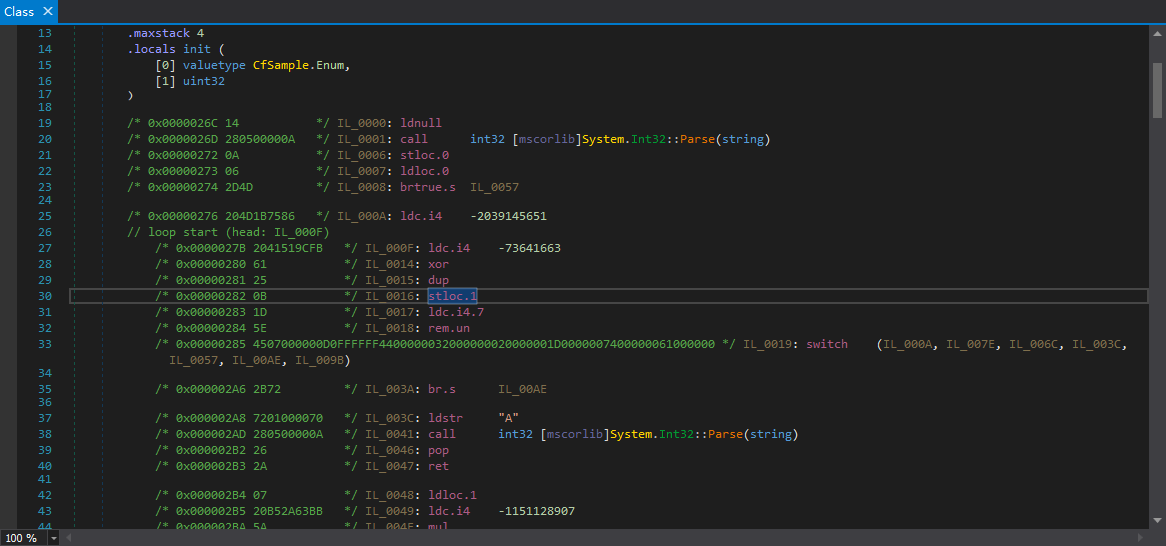
我们看看IL:
只用到了局部变量V_1。
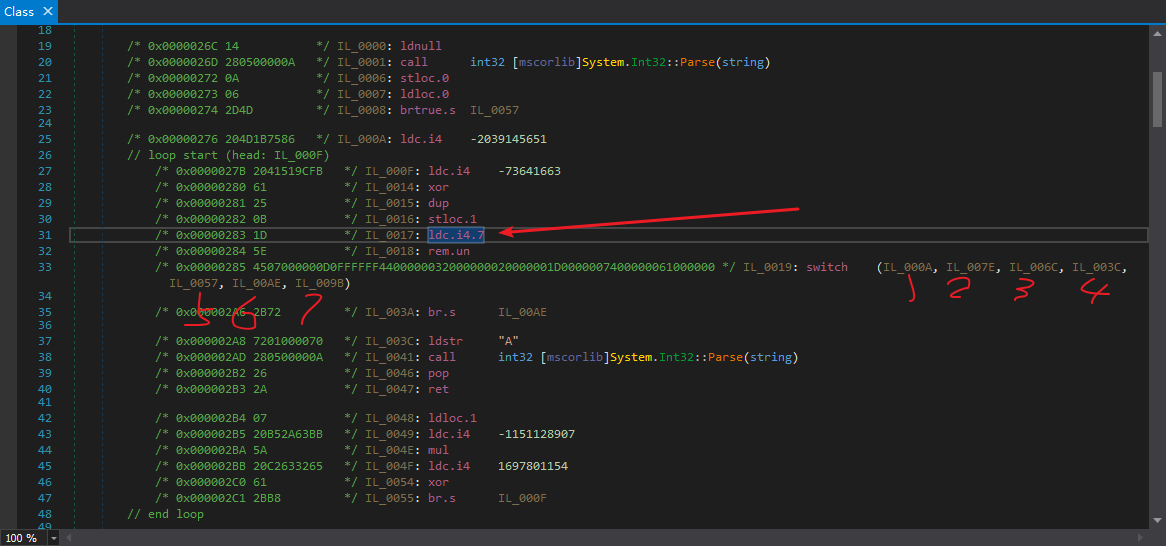
为什么ConfuserEx生成的控制流混淆里面的常量都特别的大?关键还是一个求余运算,比如 x % 7,那么结果的取值范围就是{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6},恰好7个结果。
比如这个switch,有7个条件跳转目标,那么就是% 7,也就是除以7求余数。
我们还会注意到,对num赋值有2种情况,一种是和num本身的值有关的,一种是无关的:
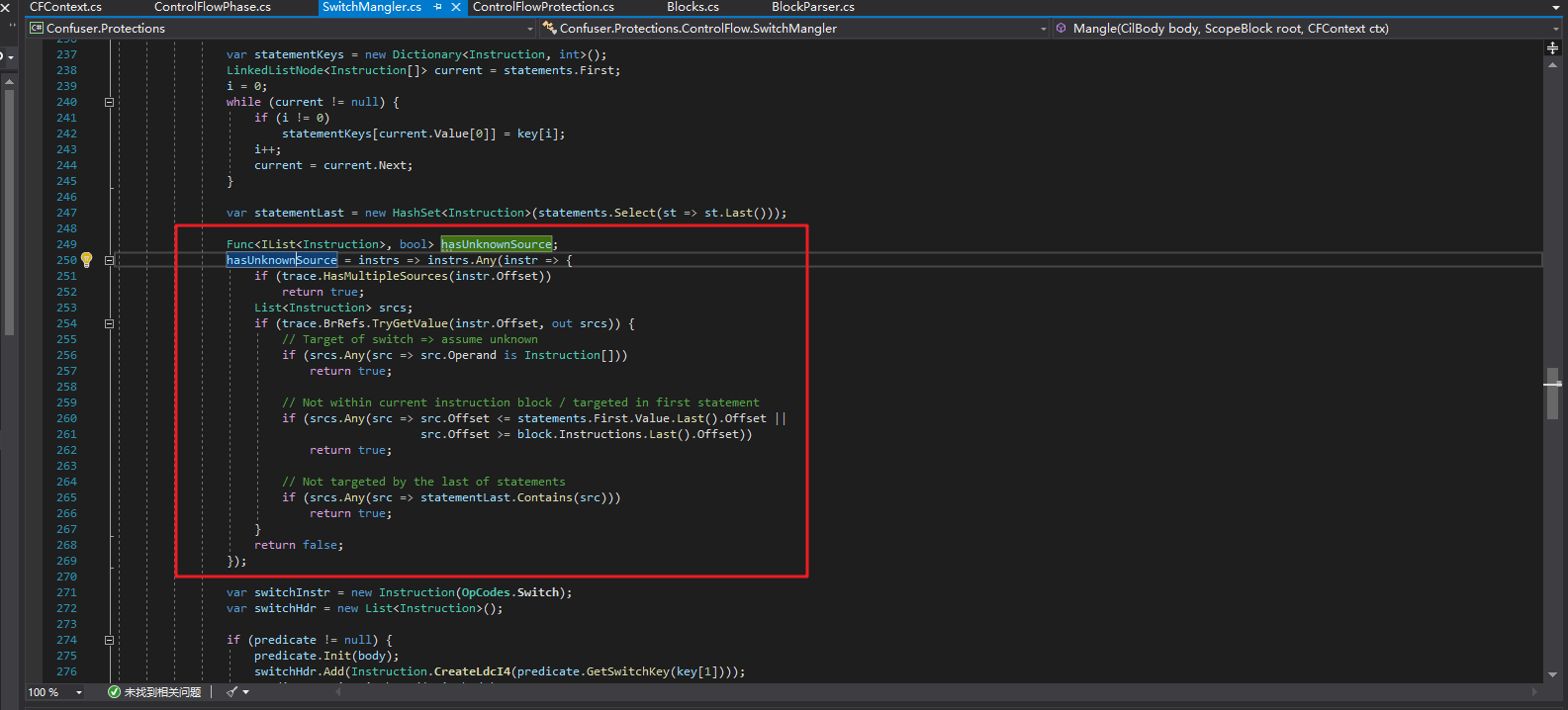
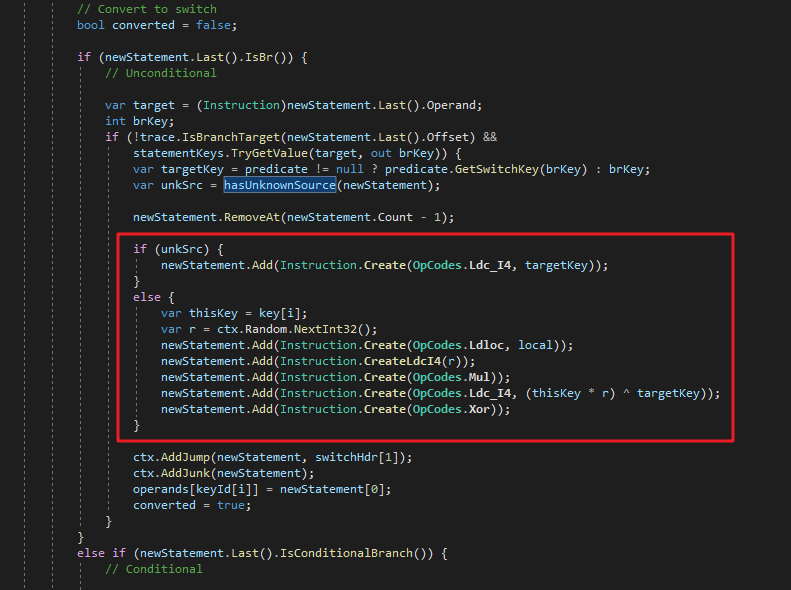
为什么会出现直接一条num = ????;就完事的代码呢?全部使用上下文相关,也就是线性编码不是强度更高么?这个肯定不是ConfuserEx作者故意的,这个也是有原因的。我们可以看看ConfuserEx源码,在这里可以找到答案:
这段代码的意思是,如果一个基本块A有未知来源,意思就是有非已知的基本块会跳转基本块A,那么就不生成线性解码的代码。因为如果是一个未知的基本块跳转到了基本块A,那么此时的num的值是不确定的,如果还是用num = num * xxxx ^ xxxx;,就会导致解码出的num是错误的。
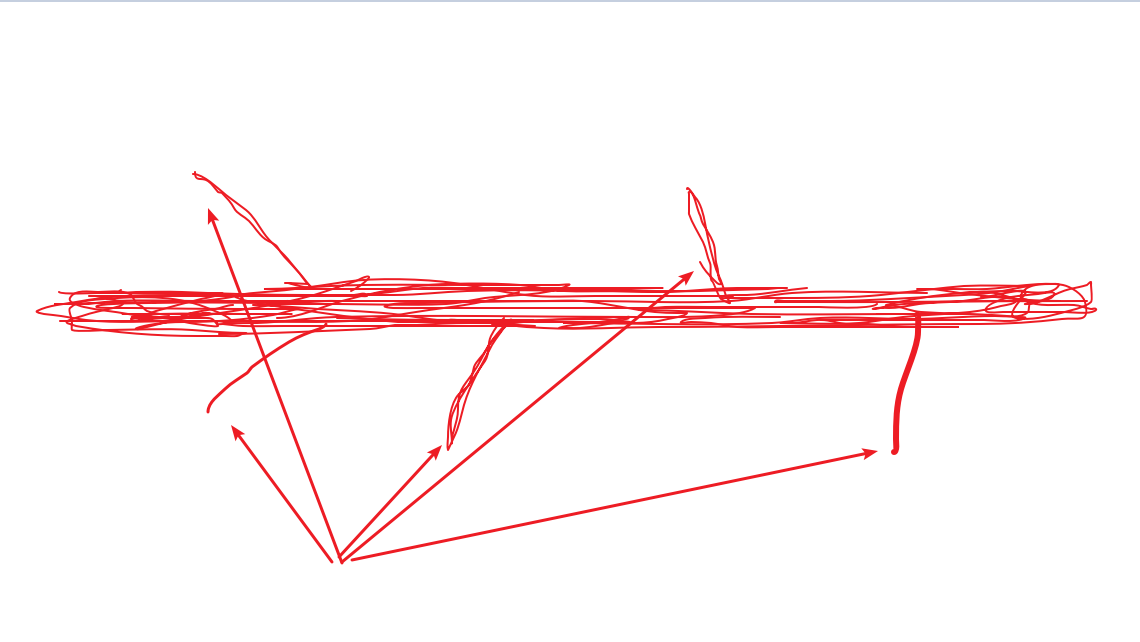
所以我们可以得出这种线性Switch混淆的一个结论:
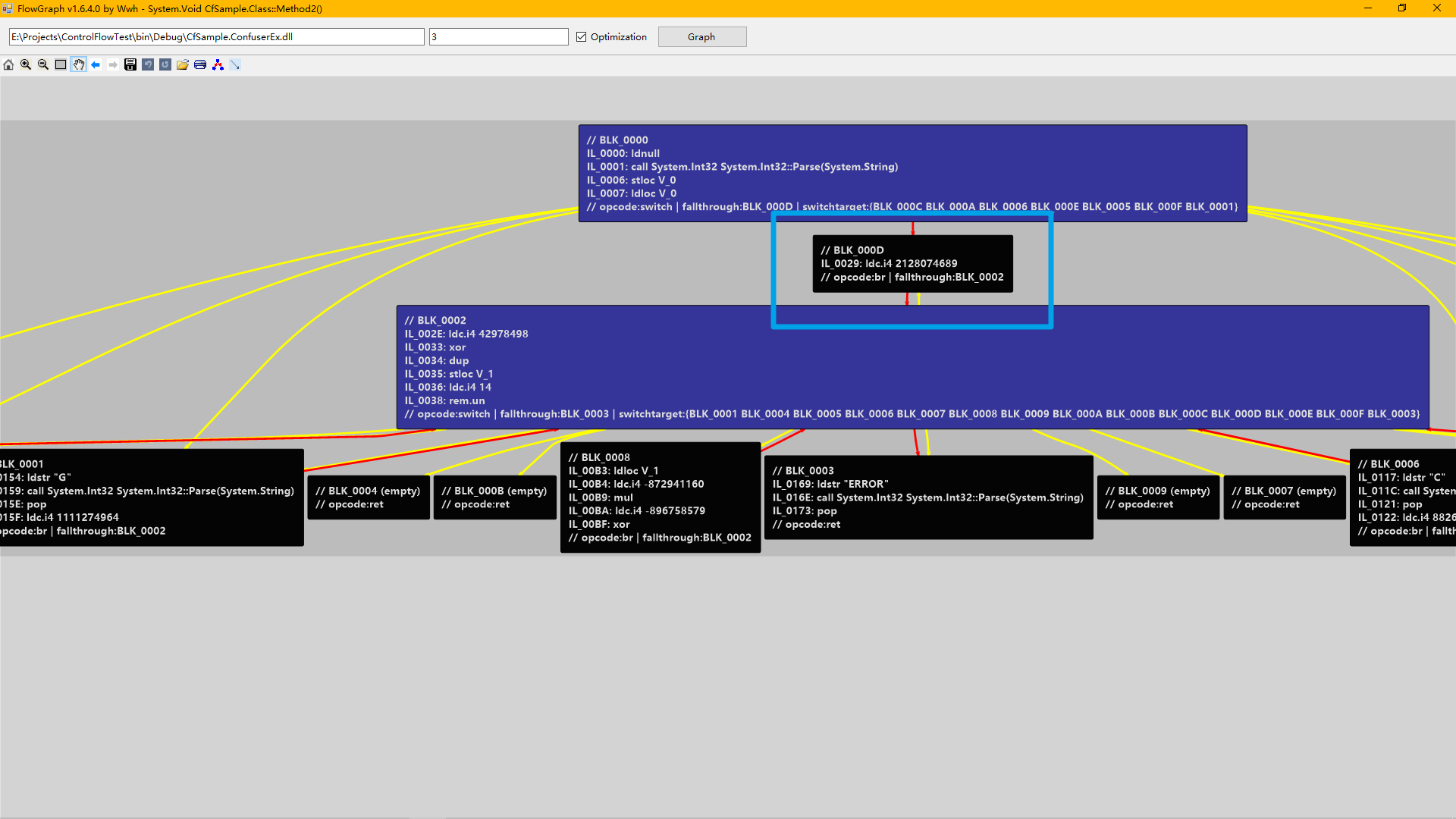
线性Switch混淆就像图中一坨混在一起的线,直接进入内部,是清理不了混淆的。而线性Switch混淆有且至少有一个为未知源准备的入口点,也就是图中箭头指着的几个很细的线条,也就是ConfuserEx Switch混淆中的直接对num进行赋值的地方。
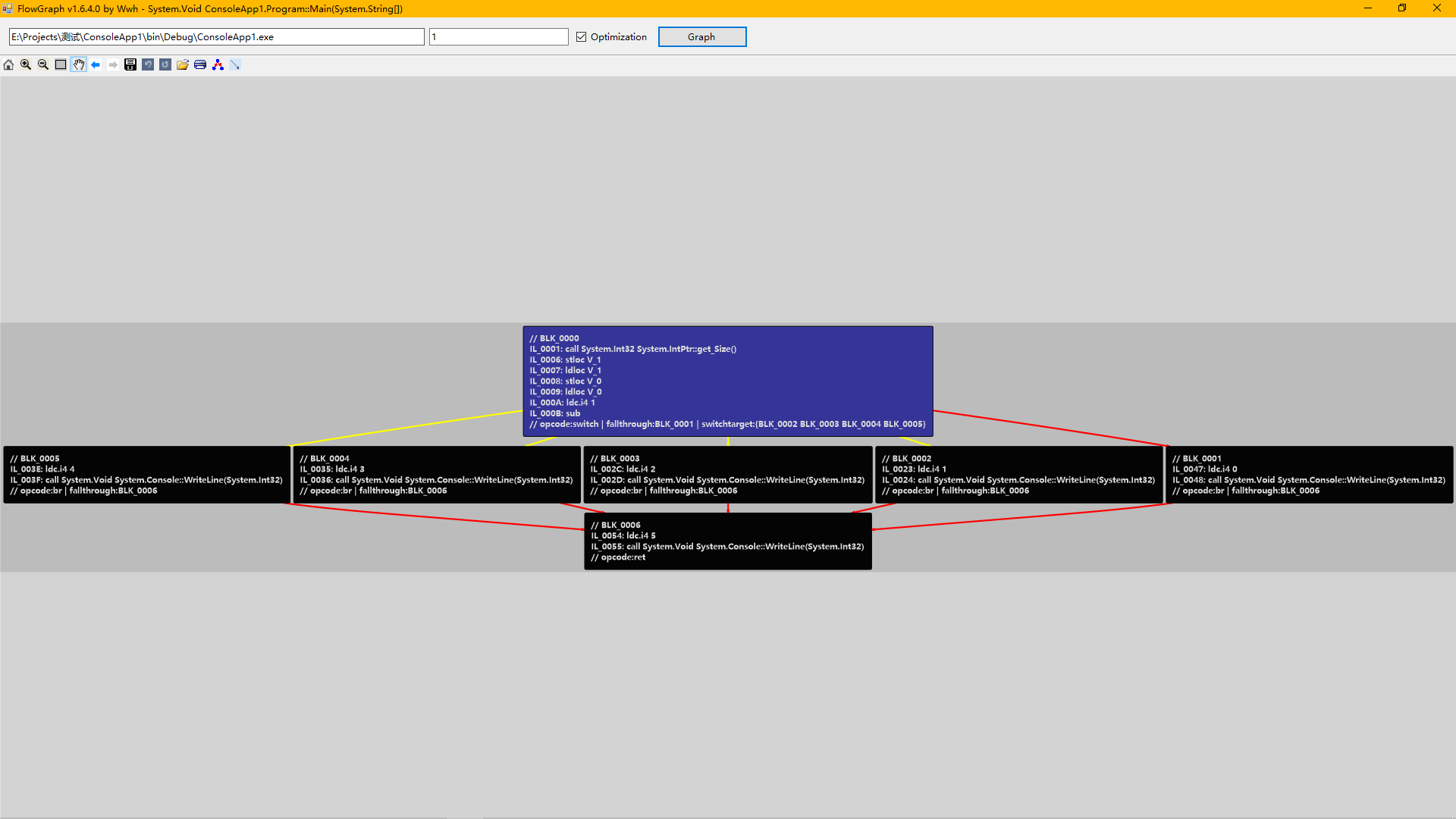
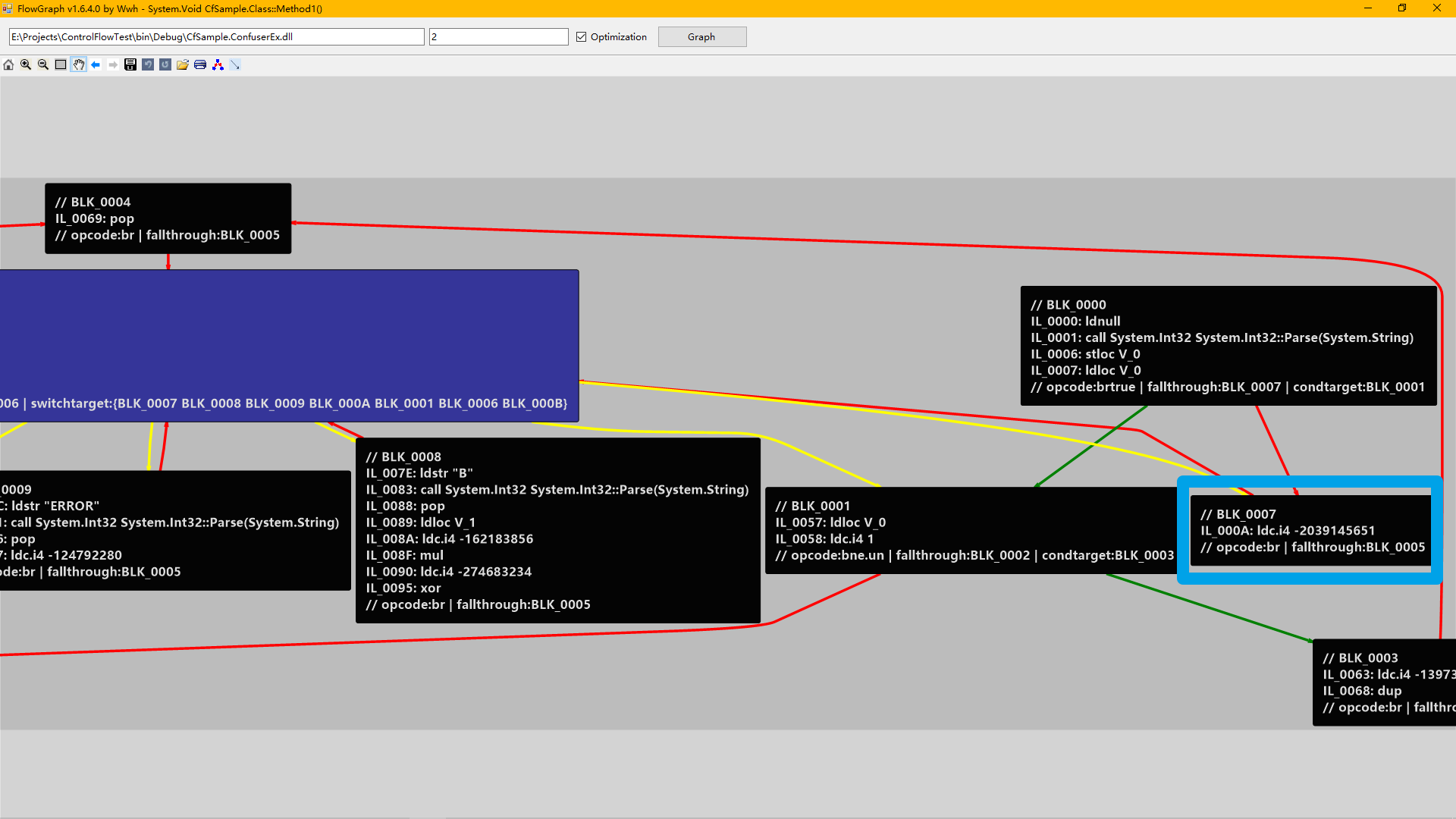
我们再用工具FlowGraph看看(开了优化的):
蓝色框圈出来的就是这个线性Switch的一个入口点。
我们可以再看看其它方法体,也是如此:
和之前总结的特征一样。
所以,我们要清理线性Switch混淆,只能从这种入口点进入,虚拟执行部分代码,才可以达到效果。
虚拟机 虚拟执行需要虚拟机。虽然有现成的虚拟机,比如de4dot.blocks里面的虚拟机,但是我就是喜欢造轮子,自己写的用着舒服,修改起来也方便,看别人的代码太累了,看懂了还要自己修改,不如从头写一个。
虚拟机完整代码文章末尾也有。
操作码分类 我们可以先对所有指令操作码进行分类,对我们需要的操作码进行模拟,不需要的就不模拟。
这里我贴上我分类好的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 Add Add_Ovf Add_Ovf_Un And Div Div_Un Mul Mul_Ovf Mul_Ovf_Un Neg Not Or Rem Rem_Un Shl Shr Shr_Un Sub Sub_Ovf Sub_Ovf_Un Xor Ceq Cgt Cgt_Un Ckfinite Clt Clt_Un Box Castclass Conv_I Conv_I1 Conv_I2 Conv_I4 Conv_I8 Conv_Ovf_I Conv_Ovf_I_Un Conv_Ovf_I1 Conv_Ovf_I1_Un Conv_Ovf_I2 Conv_Ovf_I2_Un Conv_Ovf_I4 Conv_Ovf_I4_Un Conv_Ovf_I8 Conv_Ovf_I8_Un Conv_Ovf_U Conv_Ovf_U_Un Conv_Ovf_U1 Conv_Ovf_U1_Un Conv_Ovf_U2 Conv_Ovf_U2_Un Conv_Ovf_U4 Conv_Ovf_U4_Un Conv_Ovf_U8 Conv_Ovf_U8_Un Conv_R_Un Conv_R4 Conv_R8 Conv_U Conv_U1 Conv_U2 Conv_U4 Conv_U8 Unbox Unbox_Any Dup Ldarg Ldarga Ldc_I4 Ldc_I8 Ldc_R4 Ldc_R8 Ldelem Ldelem_I Ldelem_I1 Ldelem_I2 Ldelem_I4 Ldelem_I8 Ldelem_R4 Ldelem_R8 Ldelem_Ref Ldelem_U1 Ldelem_U2 Ldelem_U4 Ldelema Ldfld Ldflda Ldftn Ldind_I Ldind_I1 Ldind_I2 Ldind_I4 Ldind_I8 Ldind_R4 Ldind_R8 Ldind_Ref Ldind_U1 Ldind_U2 Ldind_U4 Ldlen Ldloc Ldloca Ldnull Ldobj Ldsfld Ldsflda Ldstr Ldtoken Ldvirtftn Newarr Newobj Pop Starg Stelem Stelem_I Stelem_I1 Stelem_I2 Stelem_I4 Stelem_I8 Stelem_R4 Stelem_R8 Stelem_Ref Stfld Stind_I Stind_I1 Stind_I2 Stind_I4 Stind_I8 Stind_R4 Stind_R8 Stind_Ref Stloc Stobj Stsfld Beq Bge Bge_Un Bgt Bgt_Un Ble Ble_Un Blt Blt_Un Bne_Un Br Brfalse Brtrue Endfilter Endfinally Leave Ret Rethrow Switch Throw Call Calli Callvirt Arglist Cpblk Cpobj Initblk Initobj Isinst Localloc Mkrefany Refanytype Refanyval Sizeof
比如处理ConfuserEx控制流混淆,我们实现部分取值赋值,分配指令的虚拟化,还有所有运算指令的虚拟化就够了,非常简单。
虚拟值 我把虚拟机中的值分成了几种常见类型:
再写一个一个接口,表示虚拟值就行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 public enum ValueType { Object, Int32, Int64, Null, Unknown, Array, User } public interface IValue { ValueType Type { get ; set ; } IValue Clone () ; }
架构 我用的是de4dot.blocks里面的架构,稍微修改了一下,把虚拟机和上下文(Context)本身分离了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 public sealed class EmulationContext { private readonly Dictionary<Local, IValue> _variables; private readonly Stack<IValue> _evaluationStack; public Dictionary<Local, IValue> Variables => _variables; public Stack<IValue> EvaluationStack => _evaluationStack; public EmulationContext () _evaluationStack = new Stack<IValue>(); _variables = new Dictionary<Local, IValue>(); } public EmulationContext (IEnumerable<Local> variables ) : this () if (variables == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (variables)); foreach (Local variable in variables) _variables.Add(variable, null ); } private EmulationContext (Dictionary<Local, IValue> variables, Stack<IValue> evaluationStack ) if (variables == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (variables)); if (evaluationStack == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (evaluationStack)); _variables = variables; _evaluationStack = evaluationStack; } public EmulationContext Clone () IValue[] array; Stack<IValue> evaluationStack; Dictionary<Local, IValue> variables; array = _evaluationStack.ToArray(); evaluationStack = new Stack<IValue>(_evaluationStack.Count); for (int i = array.Length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) evaluationStack.Push(array[i].Clone()); variables = new Dictionary<Local, IValue>(_variables.Count); foreach (KeyValuePair<Local, IValue> variable in _variables) variables.Add(variable.Key, variable.Value?.Clone()); return new EmulationContext(variables, evaluationStack); } } public sealed class EmulationResult { private readonly bool _success; private readonly Instruction _failedInstruction; private readonly Exception _exception; public bool Success => _success; public Instruction FailedInstruction => _failedInstruction; public Exception Exception => _exception; internal EmulationResult (bool success, Instruction failedInstruction, Exception exception _success = success; _failedInstruction = failedInstruction; _exception = exception; } }
给虚拟机一个上下文,传入要虚拟执行的指令,返回执行结果,就是这么简单,并不复杂。
比如我们要虚拟执行运算指令,我们要用好C#的lambda。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 private bool Template_Arithmetic (Func<int , int , int > operation32, Func<long , long , long > operation64 ) IValue x; IValue y; IValue result; y = EvaluationStack.Pop(); x = EvaluationStack.Pop(); result = CheckAndTryGetUnknownValue_Arithmetic(x, y); if (result != null ) { EvaluationStack.Push(result); return true ; } if (x is Int32Value && y is Int32Value) { if (operation32 == null ) ThrowNotImpl(); result = new Int32Value(operation32(((Int32Value)x).Int32, ((Int32Value)y).Int32)); } else { if (operation32 == null ) ThrowNotImpl(); result = new Int64Value(operation64(GetInt64_Arithmetic(x), GetInt64_Arithmetic(y))); } EvaluationStack.Push(result); return true ; } private static IValue CheckAndTryGetUnknownValue_Arithmetic (IValue x ) if (!(x is Int32Value) && !(x is Int64Value)) ThrowErrorType(); if (x.Type == ValueType.Unknown) return x is Int32Value ? (IValue)Int32Value.Unknown : Int64Value.Unknown; else return null ; } private static IValue CheckAndTryGetUnknownValue_Arithmetic (IValue x, IValue y ) if ((!(x is Int32Value) && !(x is Int64Value)) || (!(y is Int32Value) && !(y is Int64Value))) ThrowErrorType(); if (x.Type == ValueType.Unknown || y.Type == ValueType.Unknown) return x is Int32Value ? (IValue)Int32Value.Unknown : Int64Value.Unknown; else return null ; } private static long GetInt64_Arithmetic (IValue value ) return value is Int32Value ? ((Int32Value)value ).Int32 : ((Int64Value)value ).Int64; }
要模拟运算指令,调用Template_Arithmetic就行,非常简单。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 protected virtual bool Emulate_Add (Instruction instruction ) return Template_Arithmetic((x, y) => x + y, (x, y) => x + y); } protected virtual bool Emulate_And (Instruction instruction ) return Template_Arithmetic((x, y) => x & y, (x, y) => x & y); } protected virtual bool Emulate_Div (Instruction instruction ) return Template_Arithmetic((x, y) => x / y, (x, y) => x / y); }
剩下的非常简单,就是大循环套着Switch判断操作码,然后调用对应的方法进行虚拟执行,代码不贴了。
清除 有了虚拟机之后,我们要清除Switch混淆就方便很多了。我们可以开始清除Switch混淆了。
先把部分情况进行特殊处理。
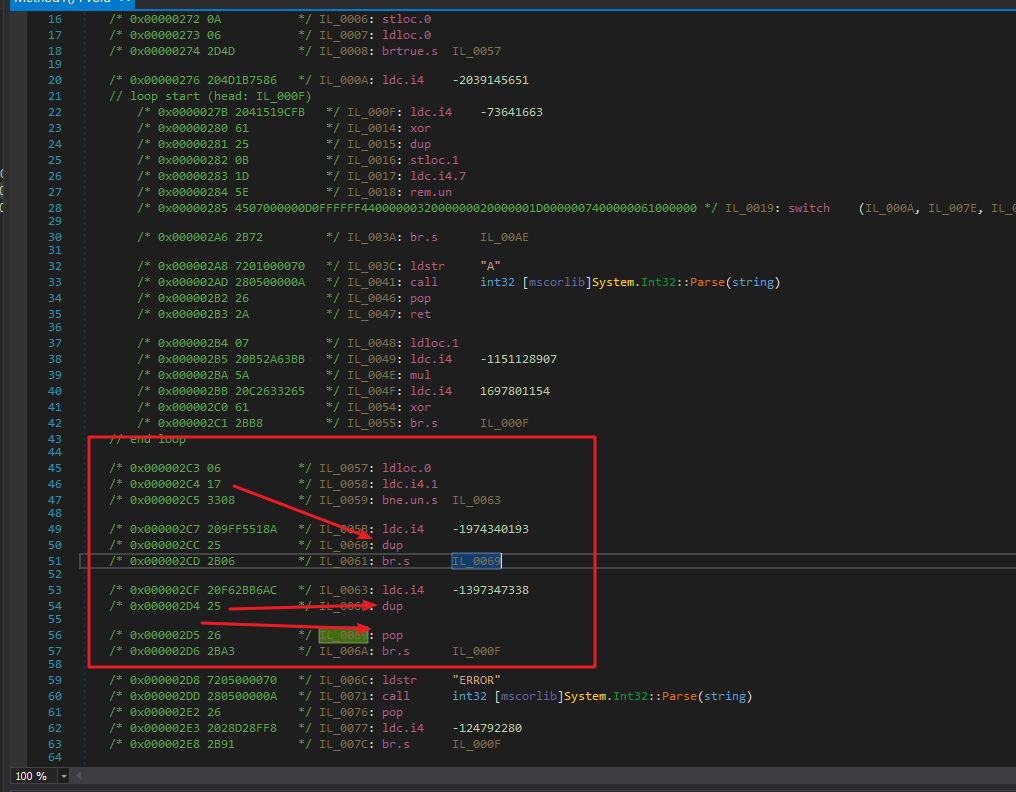
ConfuserEx会把条件跳转指令转换成这样的形式:
这里的dup和pop就是ConfuserEx故意干扰我们的代码,这里的dup和pop完全可以直接移除。
移除这种dup和pop的核心代码(其它代码没贴,了解个思路就行):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 private void HandleMultiDupWithOnePop (BasicBlock popBlock ) int popCount; List<BasicBlock> dupBlocks; int dupCount; popCount = GetPopCount(popBlock); if (popCount == 0 ) return ; dupBlocks = popBlock.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().Dereferences; if (dupBlocks.Count == 0 ) return ; foreach (BasicBlock dupBlock in dupBlocks) if (dupBlock.BranchOpcode.Code != Code.Br) return ; dupCount = int .MaxValue; foreach (BasicBlock dupBlock in dupBlocks) { int temp; temp = GetDupCount(dupBlock); if (temp < dupCount) dupCount = temp; } if (dupCount == 0 ) return ; if (popCount < dupCount) dupCount = popCount; popBlock.Instructions.RemoveRange(0 , dupCount); foreach (BasicBlock dupBlock in dupBlocks) dupBlock.Instructions.RemoveRange(dupBlock.Instructions.Count - dupCount, dupCount); _dupCount += dupCount; }
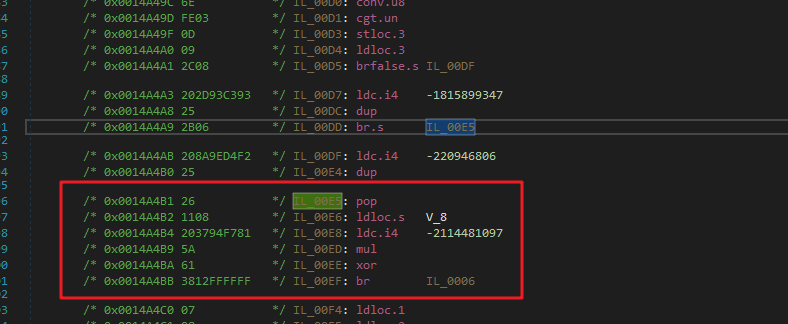
和之前的BlockInliner一样,我们还要对ConfuserEx混淆过的If进行内联,方便我们标记要模拟的指令来进行清理。
比如这种,红框中的基本块可以内联到上面2个基本块中。
我们要先定义一个抽象类,写清理线性Switch混淆的逻辑,而识别部分放到子类里面进行实现,达到代码复用。
抽象类的代码我直接贴上来了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 public abstract class LinearSwitchDeobfuscatorBase : BlockRecursiveModel { protected readonly Emulator _emulator; protected BasicBlock _switchBlock; private bool _isModified; protected LinearSwitchDeobfuscatorBase (List<IBlock> blocks, IBlock scope, EmulationContext emulationContext ) : base (blocks, scope ) _emulator = new Emulator(emulationContext); } protected static bool Deobfuscate (MethodBlock methodBlock, BlockRecursiveModelCreator deobfuscatorCreator ) return Execute(methodBlock, deobfuscatorCreator); } protected override bool Execute () if (_blocks.Count < 2 ) return false ; OnBegin(); if (_switchBlock == null ) return false ; foreach (BasicBlock entry in GetEntries ()) VisitAllBasicBlocks (entry ) ; OnEnd(); return _isModified; } protected void VisitAllBasicBlocks (BasicBlock basicBlock ) BlockInfoBase blockInfo; if (basicBlock.Scope != _scope) return ; blockInfo = basicBlock.PeekExtraData<BlockInfoBase>(); if (blockInfo.IsVisited && basicBlock != _switchBlock) return ; blockInfo.IsVisited = true ; if (blockInfo.EmulationInfo != null ) { EmulationInfo emulationInfo; EmulationResult emulationResult; emulationInfo = blockInfo.EmulationInfo; _isModified |= OnEmulateBegin(basicBlock); emulationResult = _emulator.Emulate(basicBlock.Instructions, emulationInfo.StartIndex, emulationInfo.Length); _isModified |= OnEmulateEnd(basicBlock); if (!emulationResult.Success) throw new NotImplementedException("暂未实现模拟失败处理,需要更新反混淆模型,或者检查是否模拟了不需要模拟的指令" ); } if (basicBlock == _switchBlock) VisitAllBasicBlocks(GetNextBasicBlock()); else switch (basicBlock.BranchOpcode.FlowControl) { case FlowControl.Branch: VisitAllBasicBlocks(basicBlock.FallThrough); break ; case FlowControl.Cond_Branch: CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional(basicBlock); break ; } } protected abstract void OnBegin () protected abstract void OnEnd () protected abstract IEnumerable<BasicBlock> GetEntries () protected abstract bool OnEmulateBegin (BasicBlock basicBlock ) protected abstract bool OnEmulateEnd (BasicBlock basicBlock ) protected virtual BasicBlock GetNextBasicBlock () Int32Value value ; value = _emulator.EvaluationStack.Pop() as Int32Value; if (value == null ) throw new InvalidOperationException(); return _switchBlock.SwitchTargets[value .Int32]; } protected virtual void CallNextVisitAllBasicBlocksConditional (BasicBlock basicBlock ) EmulationContext context; context = _emulator.Context.Clone(); if (basicBlock.FallThrough != null ) { VisitAllBasicBlocks(basicBlock.FallThrough); _emulator.Context = context; } if (basicBlock.ConditionalTarget != null ) { VisitAllBasicBlocks(basicBlock.ConditionalTarget); _emulator.Context = context; } if (basicBlock.SwitchTargets != null ) foreach (BasicBlock target in basicBlock.SwitchTargets) { VisitAllBasicBlocks(target); _emulator.Context = context; } } protected abstract class BlockInfoBase { protected bool _isVisited; protected EmulationInfo _emulationInfo; public bool IsVisited { get => _isVisited; set => _isVisited = value ; } public EmulationInfo EmulationInfo { get => _emulationInfo; set => _emulationInfo = value ; } } protected sealed class EmulationInfo { private readonly int _startIndex; private readonly int _length; public int StartIndex => _startIndex; public int Length => _length; public EmulationInfo (int startIndex, int length _startIndex = startIndex; _length = length; } } }
代码不多,核心的部分还是在方法名带了VisitAllBasicBlocks的方法里。比如VisitAllBasicBlocks,就是模拟程序正常执行流程,遇到了Switch混淆的地方,就模拟执行,然后在OnEmulateEnd里面完成Switch混淆的解密。
做完那么多清理操作,ConfuserEx的Switch差不多原形毕露了,特征变得非常明显,我们继承LinearSwitchDeobfuscatorBase再识别一下特征就可以了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 public sealed class LinearSwitchDeobfuscator : LinearSwitchDeobfuscatorBase { private BasicBlock _lastCaseBlockAny; private LinearSwitchDeobfuscator (List<IBlock> blocks, IBlock scope, EmulationContext emulationContext ) : base (blocks, scope, emulationContext ) } public static bool Deobfuscate (MethodBlock methodBlock ) bool isModified; isModified = false ; while (Deobfuscate(methodBlock, (blocks, scope) => new LinearSwitchDeobfuscator(blocks, scope, methodBlock.CreateEmulationContext()))) { methodBlock.Standardize(); isModified = true ; } return isModified; } protected override void OnBegin () foreach (BasicBlock basicBlock in _blocks.EnumerateAllBasicBlocks()) if (IsLinearSwitchBlock(basicBlock)) { _switchBlock = basicBlock; break ; } if (_switchBlock == null ) return ; foreach (BasicBlock basicBlock in _blocks.EnumerateAllBasicBlocks()) { if (basicBlock == _switchBlock) basicBlock.PushExtraData(new BlockInfo(BlockType.LinearSwitch) { EmulationInfo = new EmulationInfo(0 , SwitchConstants.LinearSwitchCodes.Length) }); else if (IsCaseBlock(basicBlock)) basicBlock.PushExtraData(new BlockInfo(BlockType.Case) { EmulationInfo = new EmulationInfo(basicBlock.Instructions.Count - SwitchConstants.CaseCodes.Length, SwitchConstants.CaseCodes.Length) }); else if (IsLinearCaseBlock(basicBlock)) basicBlock.PushExtraData(new BlockInfo(BlockType.LinearCase) { EmulationInfo = new EmulationInfo(basicBlock.Instructions.Count - SwitchConstants.LinearCaseCodes1.Length, SwitchConstants.LinearCaseCodes1.Length) }); else basicBlock.PushExtraData(new BlockInfo(BlockType.Normal)); } } private bool IsLinearSwitchBlock (BasicBlock basicBlock ) return basicBlock.BranchOpcode.Code == Code.Switch && basicBlock.Instructions.CodeEquals(SwitchConstants.LinearSwitchCodes); } private bool IsCaseBlock (BasicBlock basicBlock ) return basicBlock.BranchOpcode.Code == Code.Br && basicBlock.FallThrough == _switchBlock && basicBlock.Instructions.EndsWith(SwitchConstants.CaseCodes); } private bool IsLinearCaseBlock (BasicBlock basicBlock ) return basicBlock.BranchOpcode.Code == Code.Br && basicBlock.FallThrough == _switchBlock && (basicBlock.Instructions.EndsWith(SwitchConstants.LinearCaseCodes1) || basicBlock.Instructions.EndsWith(SwitchConstants.LinearCaseCodes2)); } protected override void OnEnd () foreach (BasicBlock basicBlock in _blocks.EnumerateAllBasicBlocks()) basicBlock.PopExtraData(); } protected override IEnumerable <BasicBlock > GetEntries () foreach (BasicBlock basicBlock in _blocks.EnumerateAllBasicBlocks()) if (basicBlock.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>().Type == BlockType.Case) yield return basicBlock; } protected override bool OnEmulateBegin (BasicBlock basicBlock ) return false ; } protected override bool OnEmulateEnd (BasicBlock basicBlock ) BlockInfo blockInfo; blockInfo = basicBlock.PeekExtraData<BlockInfo>(); switch (blockInfo.Type) { case BlockType.LinearSwitch: Int32Value value ; if (_lastCaseBlockAny == null ) throw new InvalidOperationException(); value = _emulator.EvaluationStack.Peek() as Int32Value; if (value == null ) throw new InvalidOperationException(); _lastCaseBlockAny.FallThrough = _switchBlock.SwitchTargets[value .Int32]; _lastCaseBlockAny = null ; return true ; case BlockType.Case: basicBlock.Instructions.RemoveTrailingRange(SwitchConstants.CaseCodes.Length); _lastCaseBlockAny = basicBlock; break ; case BlockType.LinearCase: basicBlock.Instructions.RemoveTrailingRange(SwitchConstants.LinearCaseCodes1.Length); _lastCaseBlockAny = basicBlock; break ; } return false ; } private enum BlockType { Normal, LinearSwitch, Case, LinearCase } private sealed class BlockInfo : BlockInfoBase { private readonly BlockType _type; public BlockType Type => _type; public BlockInfo (BlockType type ) _type = type; } } }
这段代码中的清理部分在OnEmulateEnd,这个OnEmulateEnd很像一个Hook,我们在switch跳转到目标前截获当前的计算堆栈,得到switch(num)中的num,这样我们就可以知道上一个基本块要跳转到哪里了,然后我们把上一个基本块的跳转目标修改掉,就完成了一个清理操作。
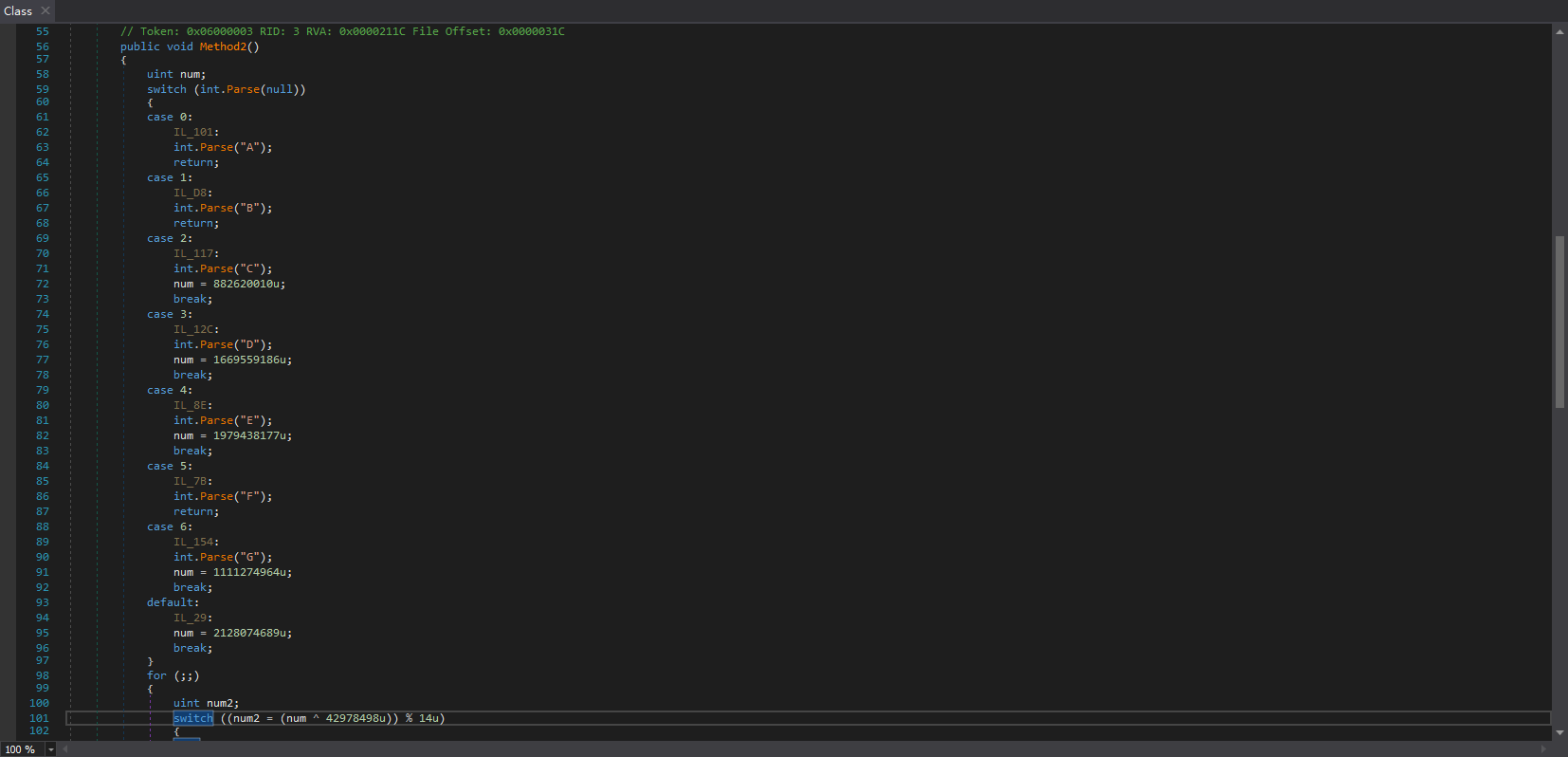
如果ConfuserEx的switch混淆加了N多层,我们还要再判断一次,是否真的是线性Switch,比如这样的,就不是线性Switch:
如果我们不先清理掉这些非线性的Switch就清理线性Switch,很可能导致出错。
下载 控制流图绘制工具FlowGraph:FlowGraph.zip
反混淆工具ConfuserExSwitchDeobfuscator:ConfuserExSwitchDeobfuscator.zip
虚拟机ControlFlow.Emulation:ControlFlow.Emulation.zip
用来测试ConfuserExSwitchDeobfuscator的UnpackMe,我加了15层控制流混淆:test.cexcf.ultimate.dnlib.dll.zip