本文介绍了.NET下的反调试原理,包括CLR内部调试机制。通过本文,可以了解到如何利用CLR调试机制进行检测和阻止调试器。
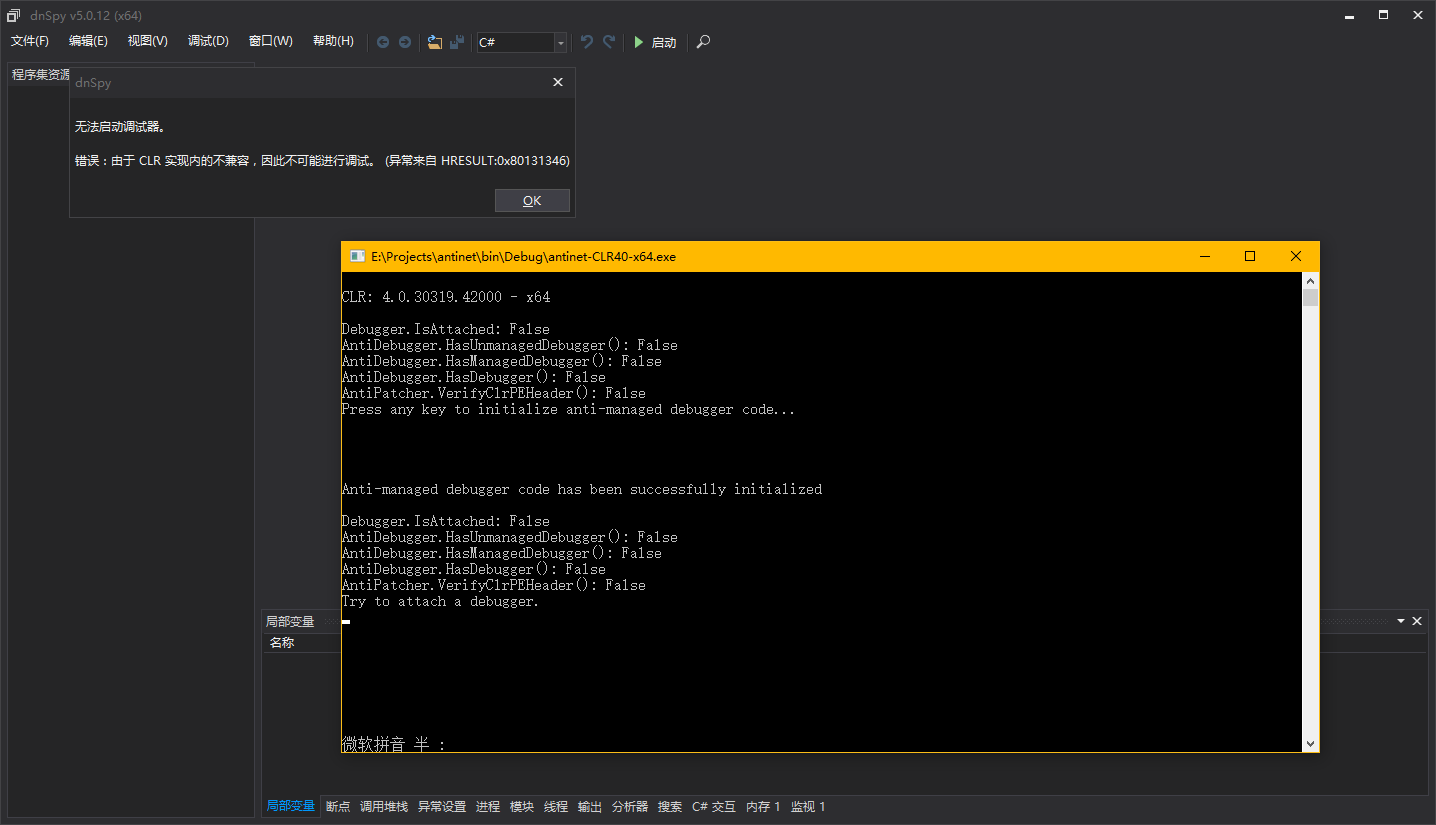
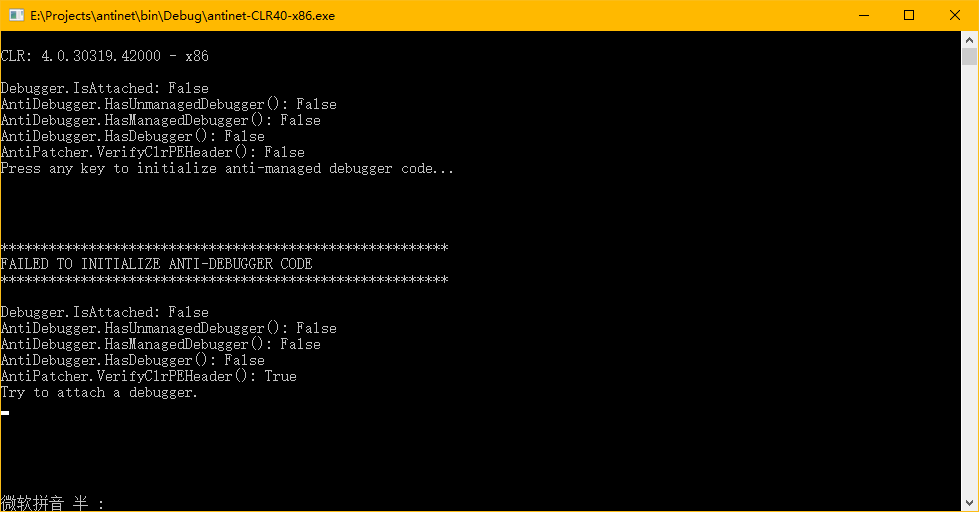
前言 0xd4d大神写过一个反调试器+反分析器的项目,叫做antinet ,代码在github上。这个反调试的原理不是检测,而是主动攻击。如果识别成功,CLR中与调试有关的一些字段将直接被破坏,让调试线程退出,其它调试器也不能附加。理论上这个反调试是几乎无解的,除非让这个反调试内部的识别机制失效。
所以我对这个代码做了一些改进,增加了Win32函数检测调试器,增加了CLR内部函数的Hook检测,顺便移除了反分析器的代码,因为那段代码对反调试没什么用,看起来也不是特别稳定。改进好的代码:https://github.com/wwh1004/antinet 。
这里先贴一下sscli20的下载地址,因为文章分析时会用到sscli20,如果没有的可以从GitHub下载。
SSCLI/sscli20_20060311
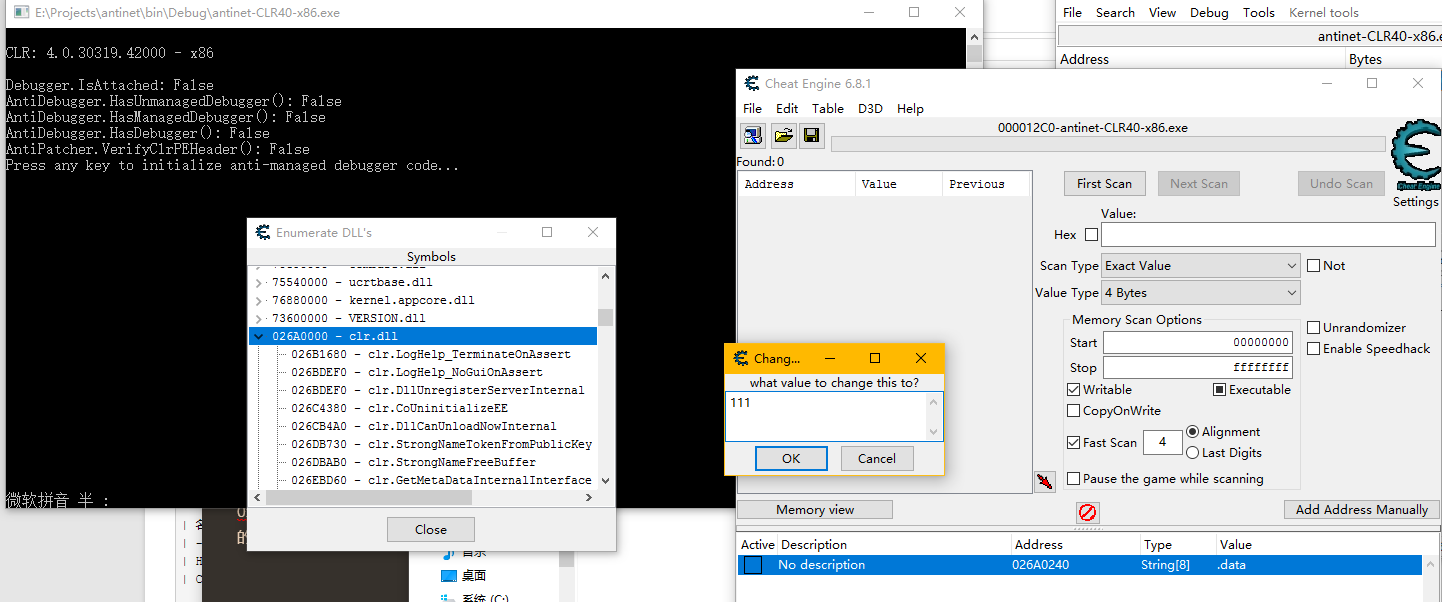
在看文章之前,请一定在vs中打开我修改过的antinet(上文有下载地址),否则可能会不清楚文章在写什么!!!
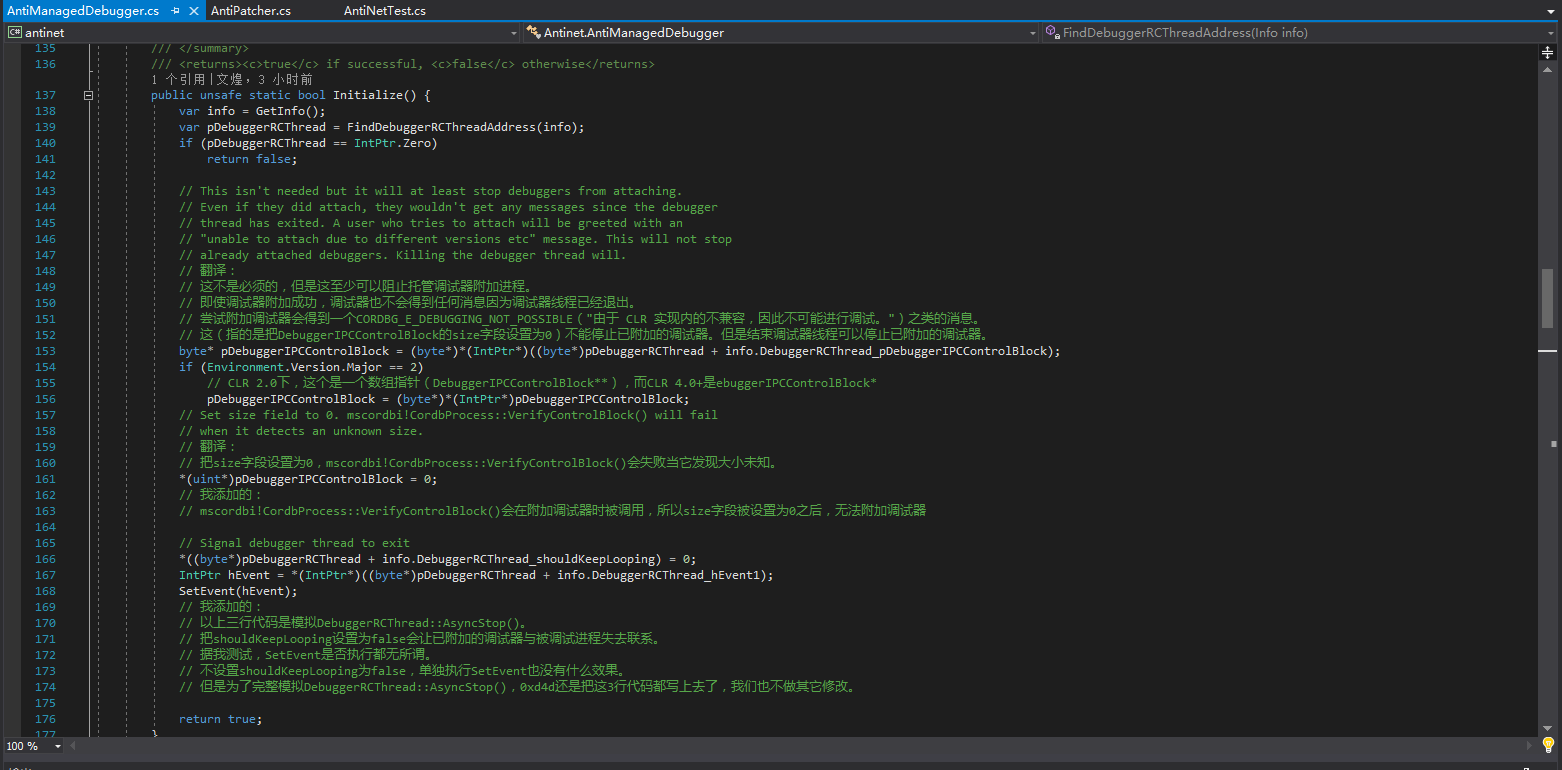
0xd4d的AntiManagedDebugger 大致流程 这个是0xd4d的antinet的反调试类,我没做修改,直接保留下来了,然后加了注释。
我们先看看0xd4d是怎么解释AntiManagedDebugger的原理。
打开https://github.com/0xd4d/antinet ,找到“Anti-managed debugger”,下面的“Technical details”(技术细节)就是实现原理。我的翻译如下(非机翻):
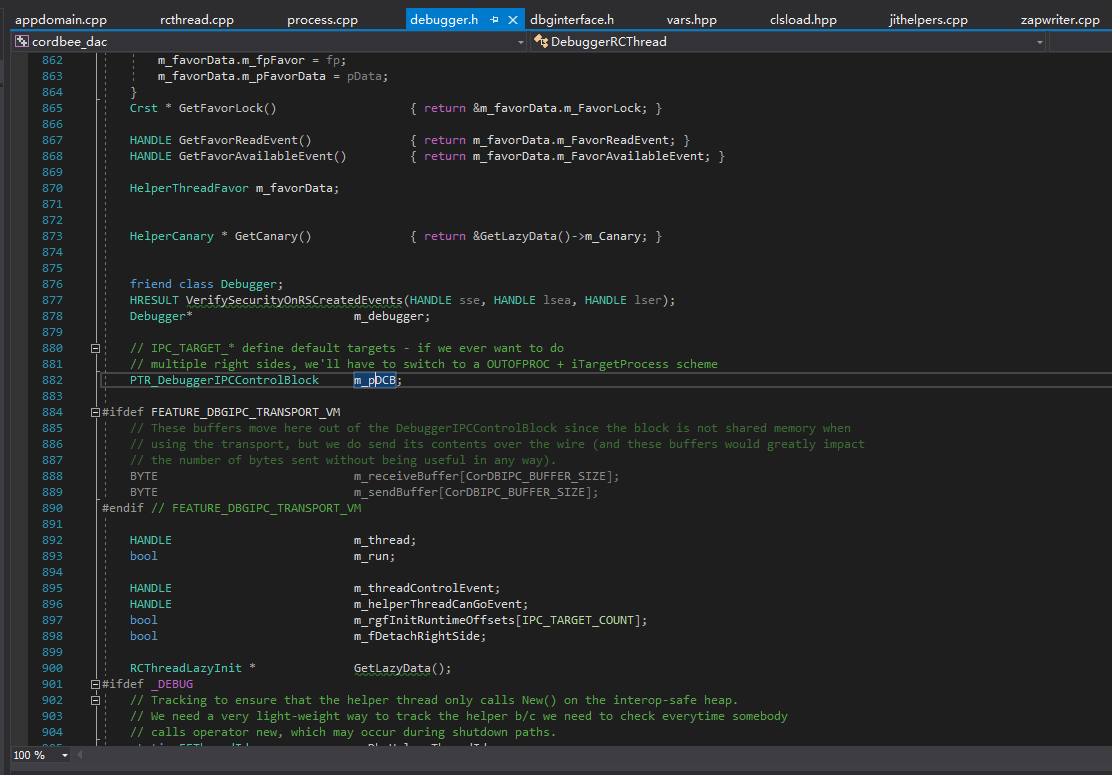
在CLR启动的时候,CLR会创建一个调试器类的实例(类名为Debugger)。这个调试器类会创建一个DebuggerRCThread类的实例,这个实例表示.NET调试器线程。正常情况下,这个线程只会在CLR退出(对一般.NET程序来说就是进程结束)时候结束。为了让这个线程提前退出,我们要将DebuggerRCThread类的实例的“keep-looping”字段设置为0并且对它进行发送信号。
这两个实例都保存在CLR的.data节。
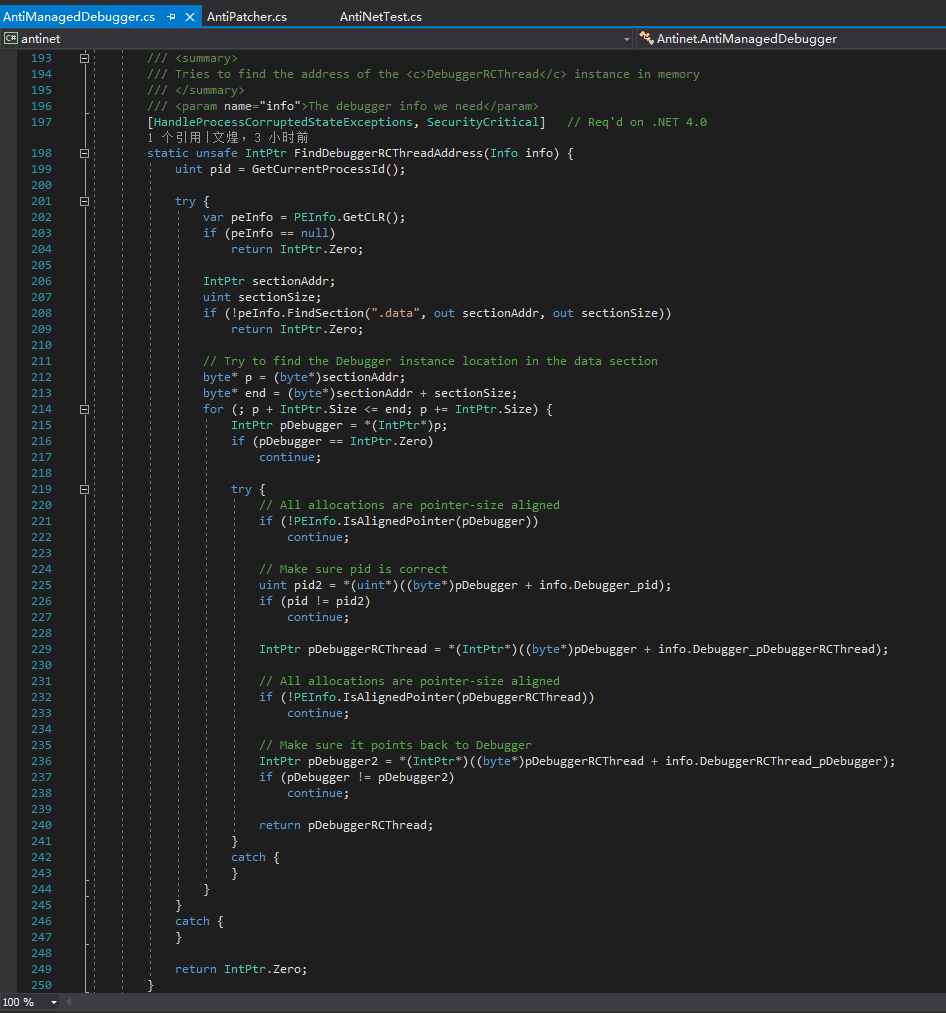
为了找到有趣的DebuggerRCThread实例,我们必须扫描.data节来获取Debugger实例的指针。我先寻找Debugger的实例是因为这个类包含了当前进程的ID,这样更易于寻找。当我们发现可能是Debugger的实例的地方出现了一些Debugger类的特征,并且这个可能的实例在指定偏移上保存了当前进程的ID,我们获取这个类中的DebuggerRCThread实例。
DebuggerRCThread类中有一个字段为指回Debugger实例的指针。如果这个指针和先前找到的Debugger实例一样,那么我们可以非常肯定我们已经找到了需要的2个实例。
一旦我们有了DebuggerRCThread实例,将keep-looping字段设置为0并且发出信号让线程退出是没有什么价值的。
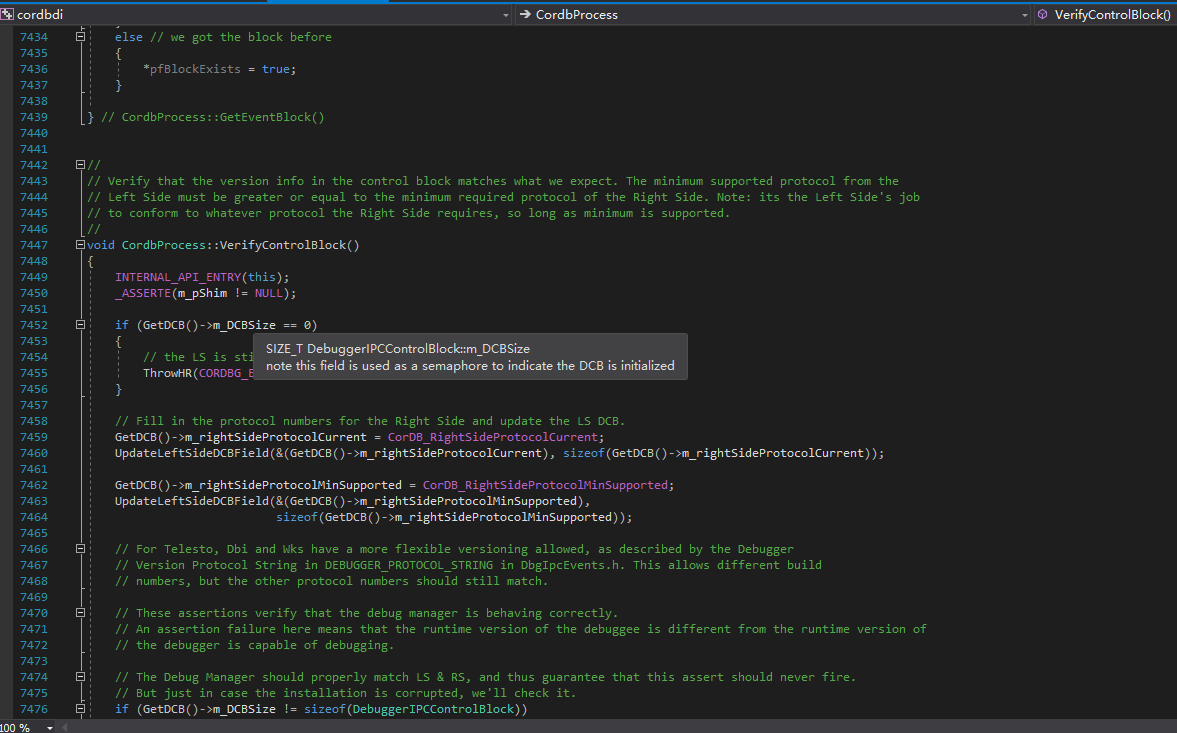
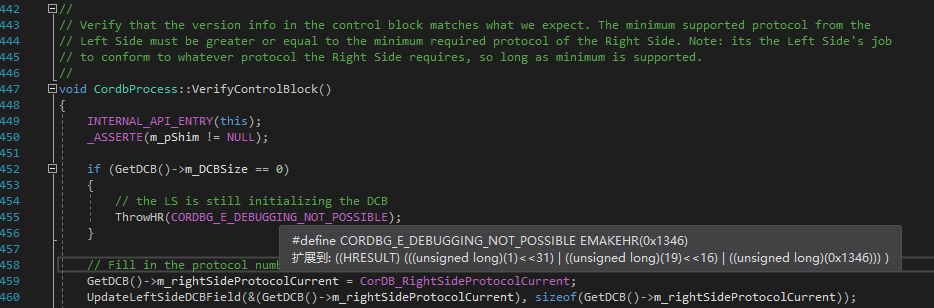
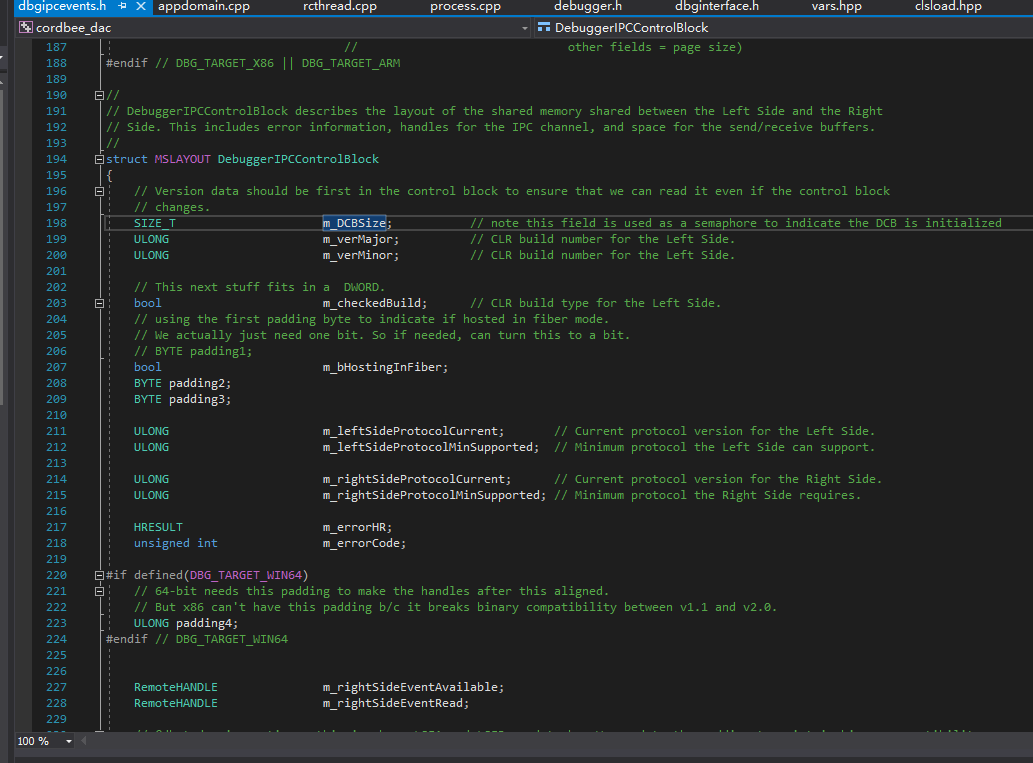
为防止调试器附加到当前进程,我们可以清除调试器IPC块的大小字段。如果这个大小字段的值被设置为其它数字了,mscordbi.dll中的CordbProcess::VerifyControlBlock()将返回一个错误代码,并且此时没有调试器能够附加当前进程了。
看不懂也没关系,大概有个印象就行。我们到vs里面看看AntiManagedDebugger类的代码。
代码的意思和0xd4d自己解释的是完全一样的,可以相互对着看,这里就不说结束调试器线程的原理和思路了,我们来看看0xd4d操作的那些字段到底是什么。
在CLR源码中了解更多 如果我没记错,CoreCLR是在CLR v4.6分支上开源的。所以CLR v4.5及之后的CLR,CoreCLR都和它们相似,看CoreCLR的源码比IDA反编译好得多。但是CLR v4.0是介于CLR v2.0和CLR v4.5之间的,可以算是一个四不像,我们暂时不管,因为现在除了XP不能装.NET 4.5,其它系统都可以装,也几乎都装了最新的.NET Framework。
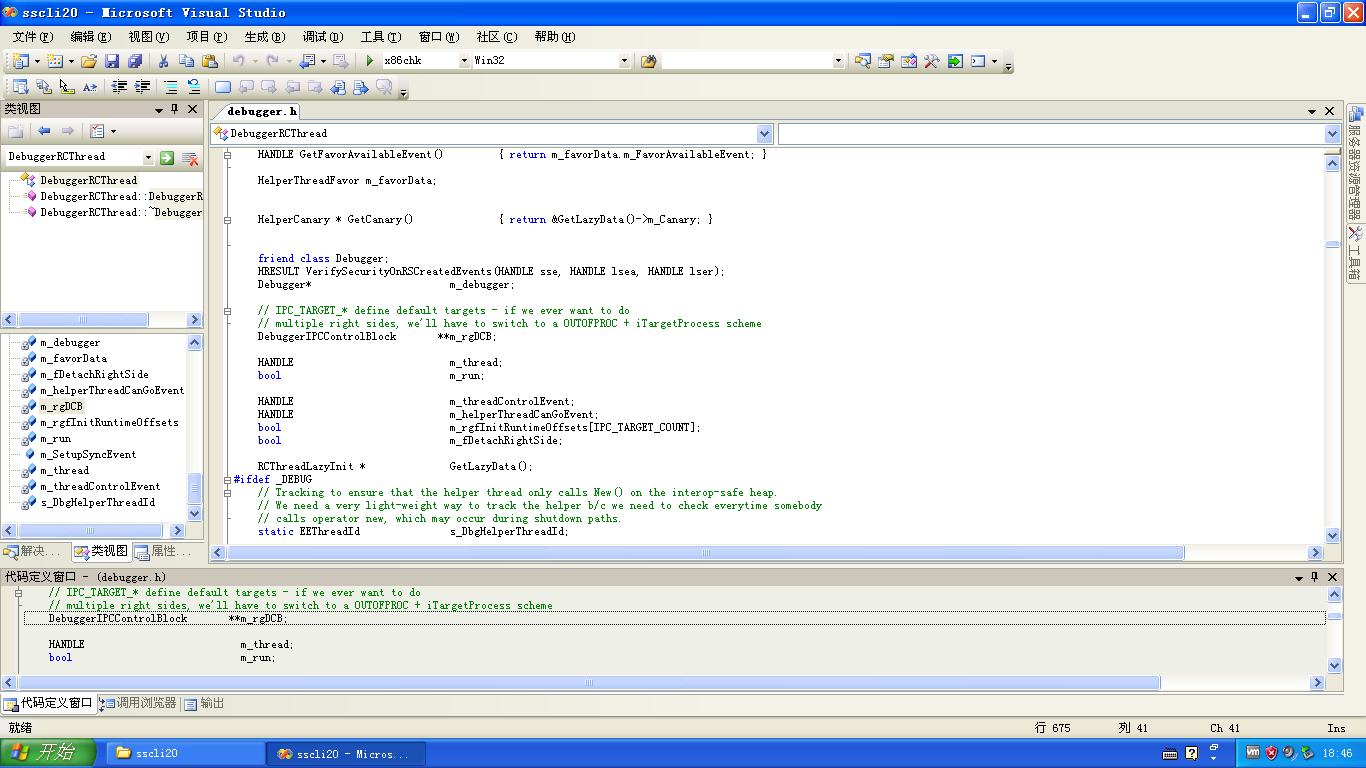
SSCLI20对应了CLR v2.0,也就是.NET 2.0~3.5。有些时候,看CLR v2.0的IDA反编译代码不如看SSCLI20的代码。
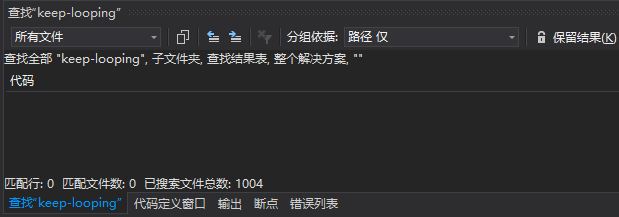
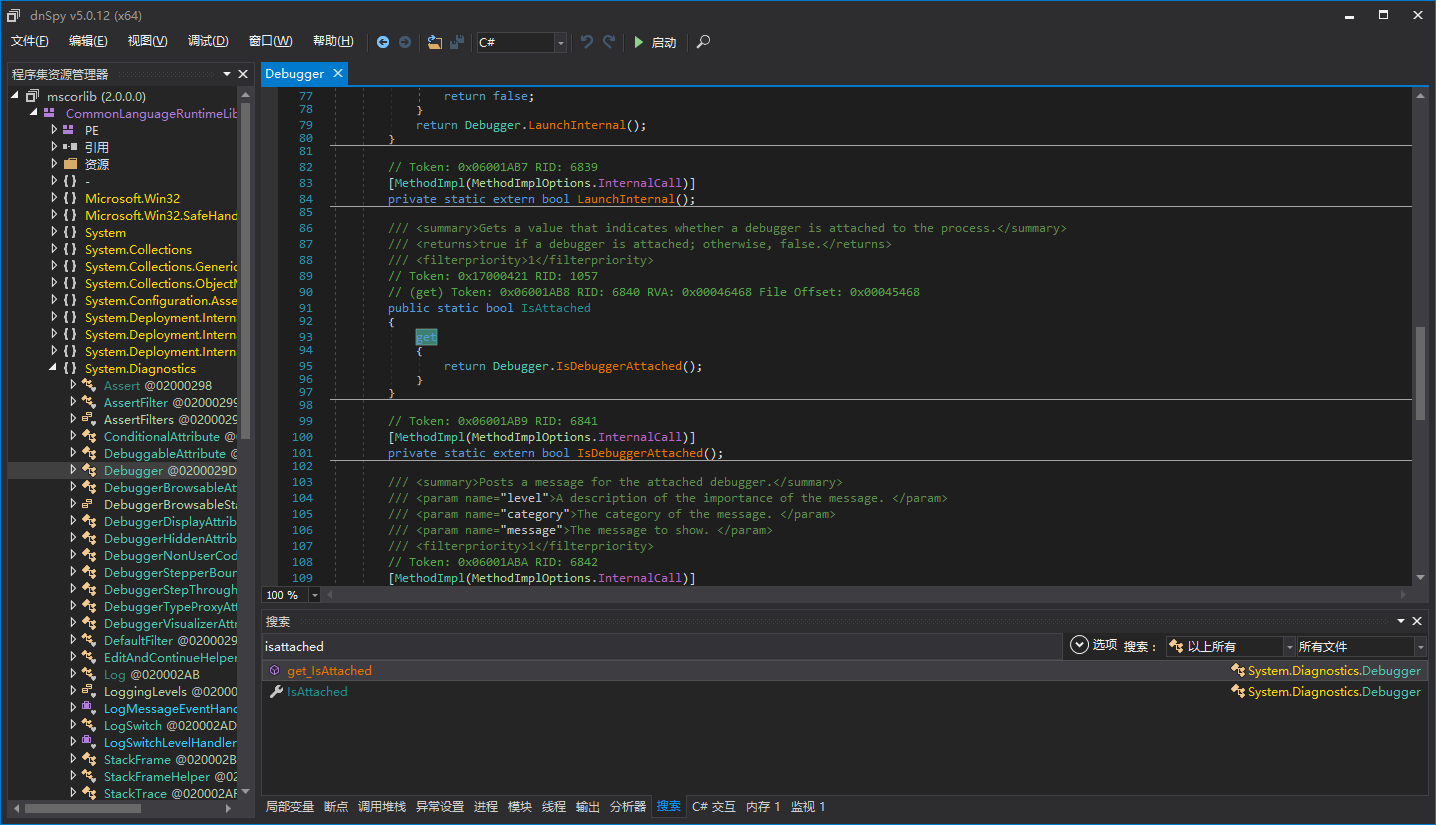
0xd4d不是提到了“keep-looping”字段么,我们在CoreCLR中找找,你会发现,其实找不到。
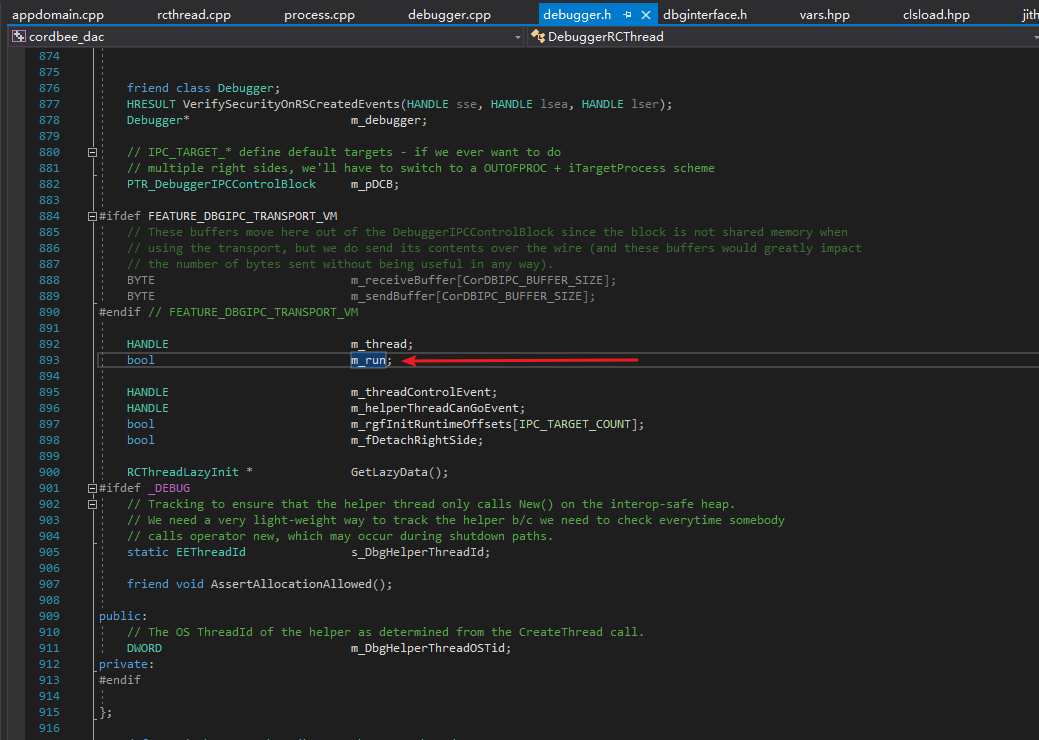
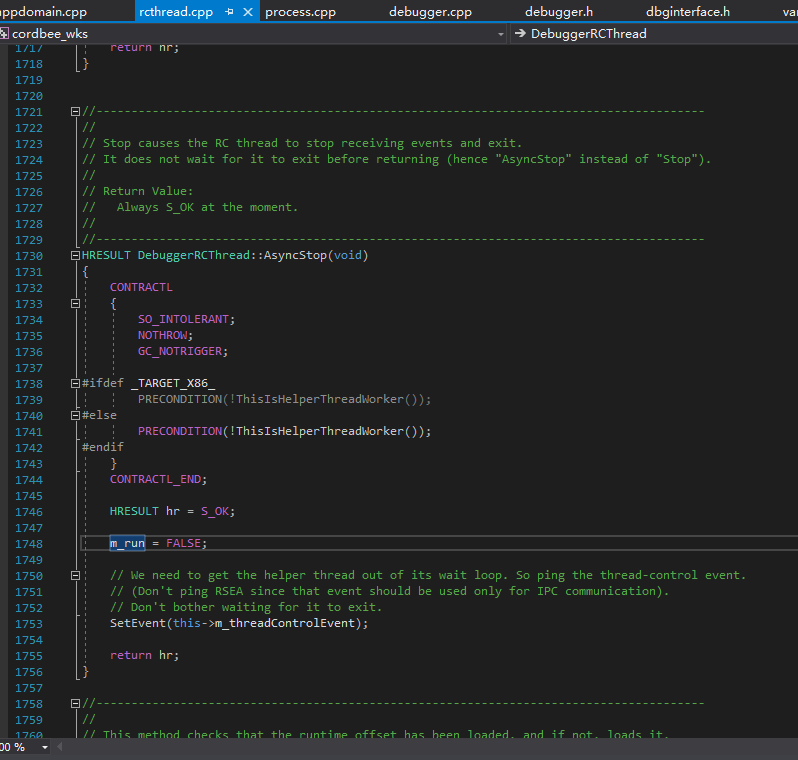
是不是0xd4d说错了呢?或者CoreCLR不一样呢?当然不是,CLR这么大型的项目,很多地方不是想改就能改的。我们仔细在DebuggerRCThread类的声明中找找,可以看到有个字段叫做“m_run”,这个字段就是0xd4d所说的“keep-looping”字段。
既然已经找到“m_run”字段了,那我们再看看AntiManagedDebugger.Initialize()的注释“Signal debugger thread to exit”对应的语句是干嘛的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 *((byte *)pDebuggerRCThread + info.DebuggerRCThread_shouldKeepLooping) = 0 ; IntPtr hEvent = *(IntPtr*)((byte *)pDebuggerRCThread + info.DebuggerRCThread_hEvent1); SetEvent(hEvent);
我们在CoreCLR中选择m_run字段,点“查找所有引用”,可以很快找到“HRESULT DebuggerRCThread::AsyncStop(void)”这个函数。
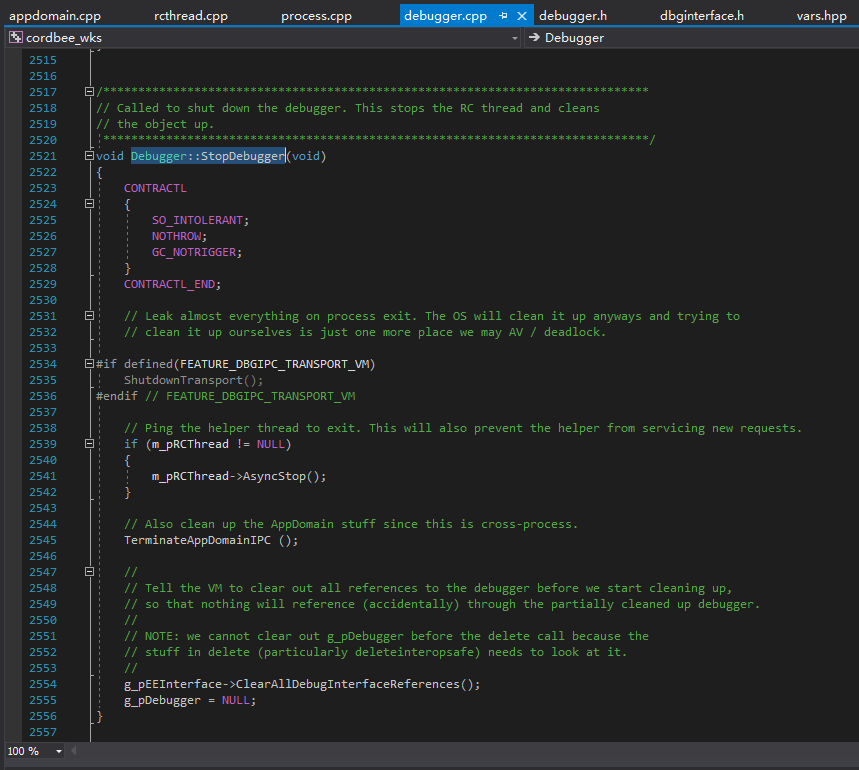
这样就弄明白了,这段代码是在模拟DebuggerRCThread::AsyncStop(),这个函数会被Debugger::StopDebugger()调用,所以可以达到结束已存在的调试器的目的。
当然了,这不能阻止托管调试器重新附加到当前进程,所以我们要在这之前,先让托管调试器不能附加当前进程。这就是以下代码的意义了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 byte * pDebuggerIPCControlBlock = (byte *)*(IntPtr*)((byte *)pDebuggerRCThread + info.DebuggerRCThread_pDebuggerIPCControlBlock);if (Environment.Version.Major == 2 ) pDebuggerIPCControlBlock = (byte *)*(IntPtr*)pDebuggerIPCControlBlock; *(uint *)pDebuggerIPCControlBlock = 0 ;
我们在CoreCLR中直接转到CordbProcess::VerifyControlBlock(),看看到底有什么样的验证。
我们再看看m_DCBSize到底被定义在了哪里,如何获取。
0xd4d的这段代码会判断当前是不是.NET 2.0~3.5,经过研究,我们可以通过SSCLI20发现一些原因。
我们先打开SSCLI20的源码。到类视图中搜索DebuggerRCThread,找到字段m_rgDCB,这个字段对应了之前的m_pDCB,只不过多了一级指针。
反反调试 0xd4d的代码是通过内存来获取.data节的地址的,我们可以直接修改节头来达到反反调试的目的。
所以我们有很多方法过掉这种反反调试,比如:
如果.data节不存在,直接退出进程,因为理论上来说.data节是一定存在的。
直接从文件中读取.data节的RVA和Size,然后再到内存中扫描对应的位置。
校验PE头有没有被修改,如果被修改了,直接退出进程。
…
其中校验PE头这个方法,是最有效的,为什么呢?既然我们不能直接删掉.data这个特征,那么我们可以伪造特征,伪造出一个假的节头,让AntiManagedDebugger修改到其它地方,而不是真正的DebuggerRCThread实例。如果我们确保PE头和文件中一致,那么我们就可以断定我们通过.data节找到DebuggerRCThread实例是真正的,有效的。
这种反反调试的方法非常容易被再次检测到,所以我们可以直接修改所有引用了这个全局变量的地方么?答案是不行。我做过各种测试,比如直接复制对象,DllMain之前或者之后修改,都会导致调试器直接出问题。
这些代码是好早之前写的,也不想再去测试了,这种方法极其麻烦,还不如直接找到反调试的地方,把它Patch掉。
改进后的Antinet AntiPatcher 既然0xd4d写的AntiManagedDebugger有一些小漏洞什么的,我们可以添加一个AntiPatcher类进行修复。
这个AntiPatcher类要可以校验CLR模块的PE头有没有被修改。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 private static void * _clrModuleHandle;private static uint _clrPEHeaderCrc32Original;private static bool _isInitialized;private static void Initialize () StringBuilder stringBuilder; byte [] clrFile; if (_isInitialized) return ; switch (Environment.Version.Major) { case 2 : _clrModuleHandle = GetModuleHandle("mscorwks.dll" ); break ; case 4 : _clrModuleHandle = GetModuleHandle("clr.dll" ); break ; default : throw new NotSupportedException(); } if (_clrModuleHandle == null ) throw new InvalidOperationException(); stringBuilder = new StringBuilder((int )MAX_PATH); if (!GetModuleFileName(_clrModuleHandle, stringBuilder, MAX_PATH)) throw new InvalidOperationException(); clrFile = File.ReadAllBytes(stringBuilder.ToString()); fixed (byte * pPEImage = clrFile) _clrPEHeaderCrc32Original = DynamicCrc32.Compute(CopyPEHeader(pPEImage)); _isInitialized = true ; } private static byte [] CopyPEHeader (void * pPEImage uint imageBaseOffset; uint length; byte [] peHeader; GetPEInfo(pPEImage, out imageBaseOffset, out length); peHeader = new byte [length]; fixed (byte * pPEHeader = peHeader) { for (uint i = 0 ; i < length; i++) pPEHeader[i] = ((byte *)pPEImage)[i]; *(void **)(pPEHeader + imageBaseOffset) = null ; } return peHeader; } private static void GetPEInfo (void * pPEImage, out uint imageBaseOffset, out uint length byte * p; ushort optionalHeaderSize; bool isPE32; uint sectionsCount; void * pSectionHeaders; p = (byte *)pPEImage; p += *(uint *)(p + 0x3C ); p += 4 + 2 ; sectionsCount = *(ushort *)p; p += 2 + 4 + 4 + 4 ; optionalHeaderSize = *(ushort *)p; p += 2 + 2 ; isPE32 = *(ushort *)p == 0x010B ; imageBaseOffset = isPE32 ? (uint )(p + 0x1C - (byte *)pPEImage) : (uint )(p + 0x18 - (byte *)pPEImage); p += optionalHeaderSize; pSectionHeaders = (void *)p; length = (uint )((byte *)pSectionHeaders + 0x28 * sectionsCount - (byte *)pPEImage); }
调用Initialize(),就可以从文件中获取CRC32。
我们再写一个方法来验证内存中是不是这样的PE头。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public static bool VerifyClrPEHeader () return DynamicCrc32.Compute(CopyPEHeader(_clrModuleHandle)) != _clrPEHeaderCrc32Original; }
AntiDebugger 首先,这个类要有原来的AntiManagedDebugger的功能,所以我们不删除AntiManagedDebugger类,直接对这个类做一个包装。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private static bool _isManagedDebuggerPrevented;public static bool PreventManagedDebugger () if (_isManagedDebuggerPrevented) return true ; _isManagedDebuggerPrevented = AntiManagedDebugger.Initialize(); return _isManagedDebuggerPrevented; }
然后我们添加一个检测非托管与托管调试器的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public static bool HasDebugger () return HasUnmanagedDebugger() || HasManagedDebugger(); }
HasUnmanagedDebugger的实现很简单,我们把xjun的XAntiDebug的syscall部分删掉就行。syscall利用漏洞的那部分改成C#代码要些时间,暂时没弄,以后有时间了再弄。毕竟非托管调试器调试.NET程序是极其痛苦的,我们的Anti目标应该主要是dnSpy等托管调试器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public static bool HasUnmanagedDebugger () bool isDebugged; if (IsDebuggerPresent()) return true ; if (!CheckRemoteDebuggerPresent(GetCurrentProcess(), &isDebugged)) return true ; if (isDebugged) return true ; try { CloseHandle((void *)0xDEADC0DE ); } catch { return true ; } return false ; }
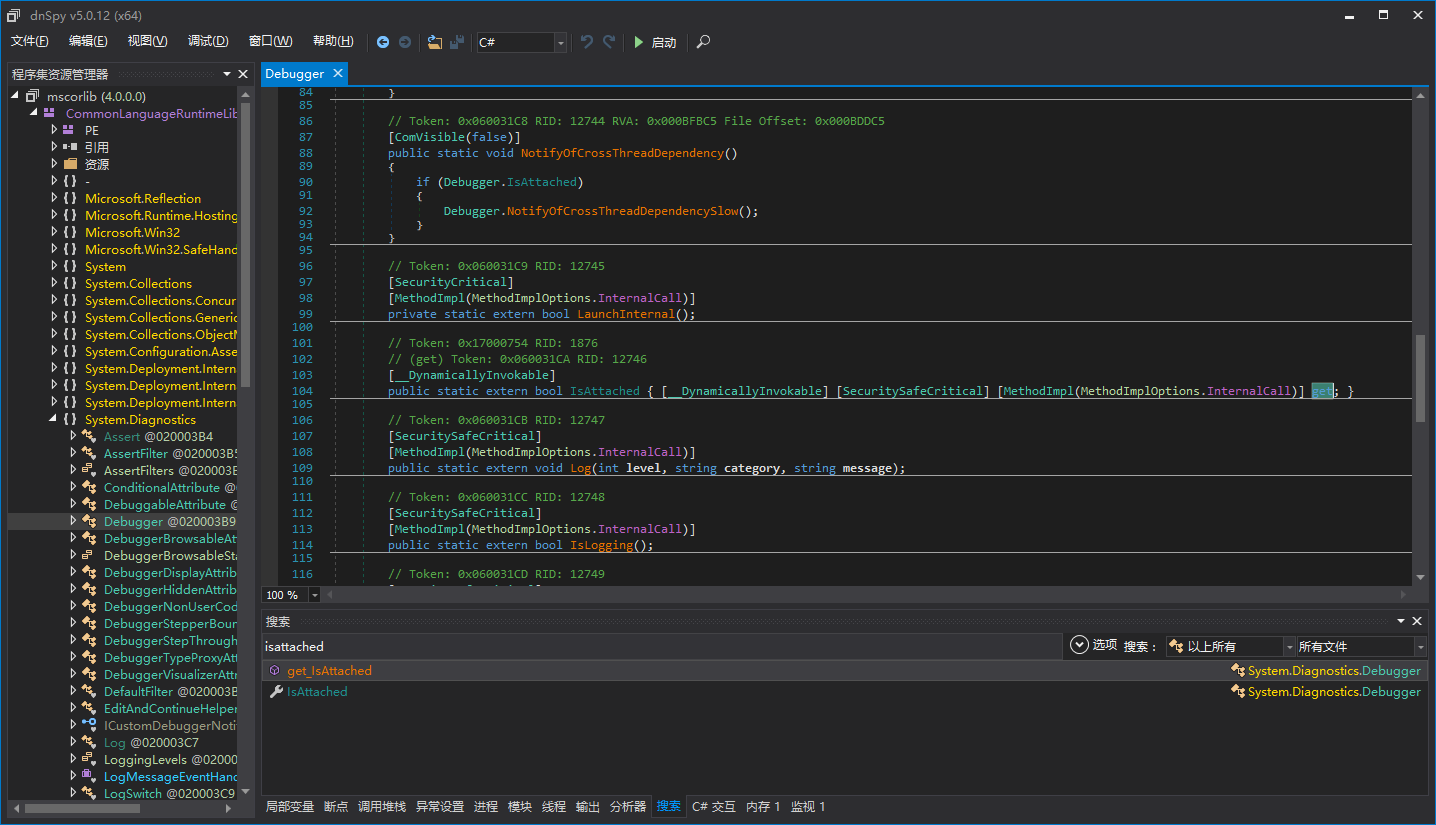
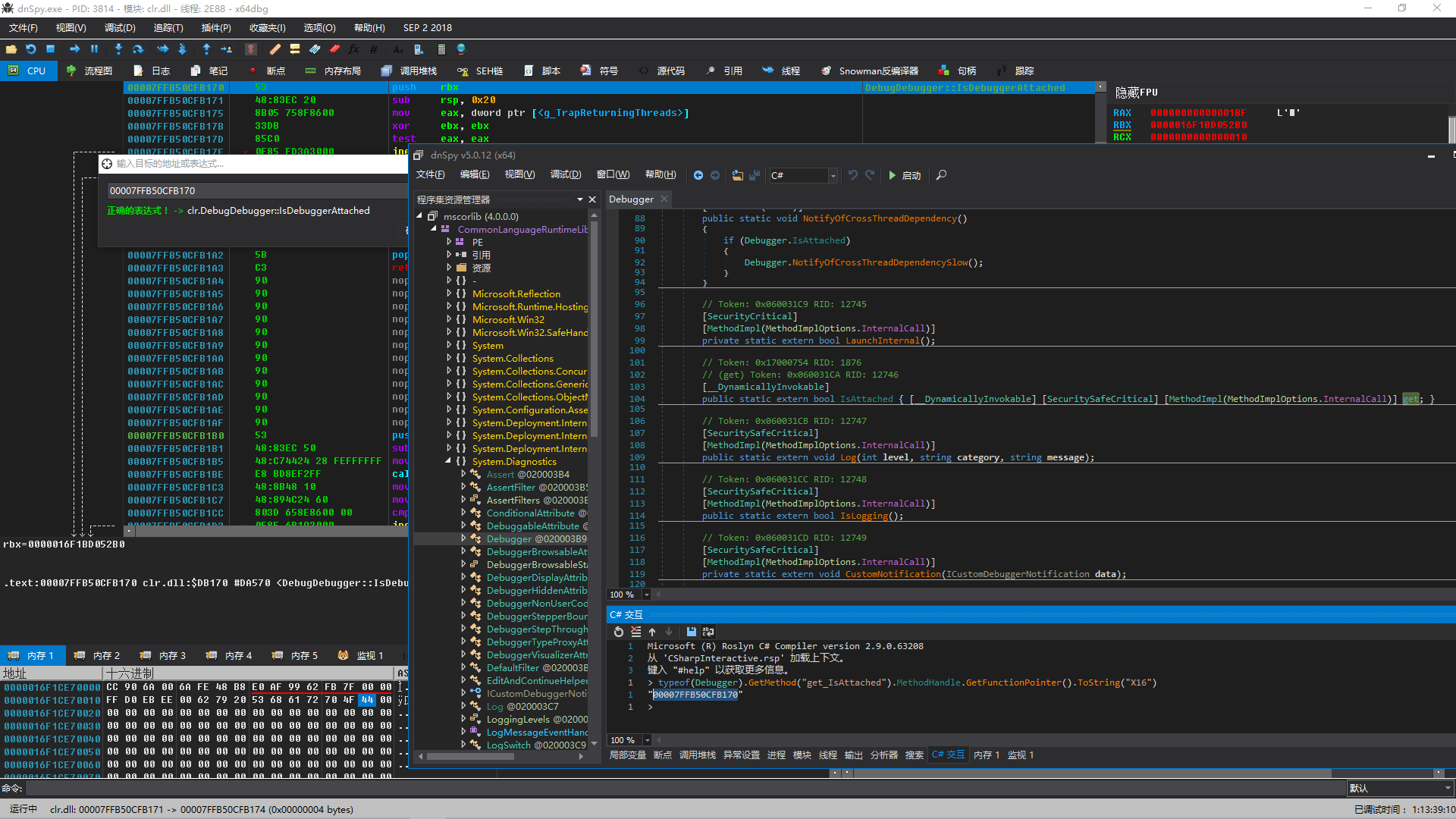
接下来是HasManagedDebugger()的实现了,这个才是重头戏。检测托管调试器最有效方便的手段是调用Debugger.IsAttached,可惜这个太容易被修改了,我们检测是否被修改就行。一个好消息是Debugger.IsAttached的实现其实在CLR内部,而且还是一个[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.InternalCall)],意思是这个方法的本机代码地址就是CLR模块中某个函数的地址。至于为什么是这样,不是本文重点,这里不做解释,可以自己研究CoreCLR。
我们添加初始化代码,直接从clr.dll/mscorwks.dll读取原始的代码,并且计算出CRC32。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 private delegate bool IsDebuggerAttachedDelegate ()private static bool _isManagedDebuggerPrevented;private static bool _isManagedInitialized;private static byte * _pIsDebuggerAttached;private static IsDebuggerAttachedDelegate _isDebuggerAttached;private static uint _isDebuggerAttachedLength;private static uint _isDebuggerAttachedCrc32;private static void InitializeManaged () void * clrModuleHandle; StringBuilder stringBuilder; byte [] clrFile; if (_isManagedInitialized) return ; switch (Environment.Version.Major) { case 2 : _pIsDebuggerAttached = (byte *)typeof (Debugger).GetMethod("IsDebuggerAttached" , BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Static).MethodHandle.GetFunctionPointer(); clrModuleHandle = GetModuleHandle("mscorwks.dll" ); break ; case 4 : _pIsDebuggerAttached = (byte *)typeof (Debugger).GetMethod("get_IsAttached" ).MethodHandle.GetFunctionPointer(); clrModuleHandle = GetModuleHandle("clr.dll" ); break ; default : throw new NotSupportedException(); } _isDebuggerAttached = (IsDebuggerAttachedDelegate)Marshal.GetDelegateForFunctionPointer((IntPtr)_pIsDebuggerAttached, typeof (IsDebuggerAttachedDelegate)); if (clrModuleHandle == null ) throw new InvalidOperationException(); stringBuilder = new StringBuilder((int )MAX_PATH); if (!GetModuleFileName(clrModuleHandle, stringBuilder, MAX_PATH)) throw new InvalidOperationException(); clrFile = File.ReadAllBytes(stringBuilder.ToString()); fixed (byte * pPEImage = clrFile) { PEInfo peInfo; uint isDebuggerAttachedRva; uint isDebuggerAttachedFoa; byte * pCodeStart; byte * pCodeCurrent; ldasm_data ldasmData; bool is64Bit; byte [] opcodes; peInfo = new PEInfo(pPEImage); isDebuggerAttachedRva = (uint )(_pIsDebuggerAttached - (byte *)clrModuleHandle); isDebuggerAttachedFoa = peInfo.ToFOA(isDebuggerAttachedRva); pCodeStart = pPEImage + isDebuggerAttachedFoa; pCodeCurrent = pCodeStart; is64Bit = sizeof (void *) == 8 ; opcodes = new byte [0x200 ]; while (true ) { uint length; length = Ldasm.ldasm(pCodeCurrent, &ldasmData, is64Bit); if ((ldasmData.flags & Ldasm.F_INVALID) != 0 ) throw new NotSupportedException(); CopyOpcode(&ldasmData, pCodeCurrent, opcodes, (uint )(pCodeCurrent - pCodeStart)); if (*pCodeCurrent == 0xC3 ) { pCodeCurrent += length; break ; } pCodeCurrent += length; } _isDebuggerAttachedLength = (uint )(pCodeCurrent - pCodeStart); fixed (byte * pOpcodes = opcodes) _isDebuggerAttachedCrc32 = DynamicCrc32.Compute(pOpcodes, _isDebuggerAttachedLength); } _isManagedInitialized = true ; } private static void CopyOpcode (ldasm_data* pLdasmData, void * pCode, byte [] opcodes, uint offset ) for (byte i = 0 ; i < pLdasmData->opcd_size; i++) opcodes[offset + pLdasmData->opcd_offset + i] = ((byte *)pCode)[pLdasmData->opcd_offset + i]; }
这里使用了Ldasm,也是看了xjun的XAntiDebug的项目才知道有这个反汇编引擎。这个反编译引擎非常小巧,真的只有1个函数,我把我翻译成的C#的代码附上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 public static uint ldasm (void * code, ldasm_data* ld, bool is64 byte * p = (byte *)code; byte s, op, f; byte rexw, pr_66, pr_67; s = rexw = pr_66 = pr_67 = 0 ; if (code == null || ld == null ) return 0 ; *ld = new ldasm_data(); while ((cflags(*p) & OP_PREFIX) != 0 ) { if (*p == 0x66 ) pr_66 = 1 ; if (*p == 0x67 ) pr_67 = 1 ; p++; s++; ld->flags |= F_PREFIX; if (s == 15 ) { ld->flags |= F_INVALID; return s; } } if (is64 && *p >> 4 == 4 ) { ld->rex = *p; rexw = (byte )((ld->rex >> 3 ) & 1 ); ld->flags |= F_REX; p++; s++; } if (is64 && *p >> 4 == 4 ) { ld->flags |= F_INVALID; s++; return s; } ld->opcd_offset = (byte )(p - (byte *)code); ld->opcd_size = 1 ; op = *p++; s++; if (op == 0x0F ) { op = *p++; s++; ld->opcd_size++; f = cflags_ex(op); if ((f & OP_INVALID) != 0 ) { ld->flags |= F_INVALID; return s; } if ((f & OP_EXTENDED) != 0 ) { op = *p++; s++; ld->opcd_size++; } } else { f = cflags(op); if (op >= 0xA0 && op <= 0xA3 ) pr_66 = pr_67; } if ((f & OP_MODRM) != 0 ) { byte mod = (byte )(*p >> 6 ); byte ro = (byte )((*p & 0x38 ) >> 3 ); byte rm = (byte )(*p & 7 ); ld->modrm = *p++; s++; ld->flags |= F_MODRM; if (op == 0xF6 && (ro == 0 || ro == 1 )) f |= OP_DATA_I8; if (op == 0xF7 && (ro == 0 || ro == 1 )) f |= OP_DATA_I16_I32_I64; if (mod != 3 && rm == 4 && !(!is64 && pr_67 != 0 )) { ld->sib = *p++; s++; ld->flags |= F_SIB; if ((ld->sib & 7 ) == 5 && mod == 0 ) { ld->disp_size = 4 ; } } switch (mod) { case 0 : if (is64) { if (rm == 5 ) { ld->disp_size = 4 ; if (is64) ld->flags |= F_RELATIVE; } } else if (pr_67 != 0 ) { if (rm == 6 ) ld->disp_size = 2 ; } else { if (rm == 5 ) ld->disp_size = 4 ; } break ; case 1 : ld->disp_size = 1 ; break ; case 2 : if (is64) ld->disp_size = 4 ; else if (pr_67 != 0 ) ld->disp_size = 2 ; else ld->disp_size = 4 ; break ; } if (ld->disp_size != 0 ) { ld->disp_offset = (byte )(p - (byte *)code); p += ld->disp_size; s += ld->disp_size; ld->flags |= F_DISP; } } if (rexw != 0 && (f & OP_DATA_I16_I32_I64) != 0 ) ld->imm_size = 8 ; else if ((f & OP_DATA_I16_I32) != 0 || (f & OP_DATA_I16_I32_I64) != 0 ) ld->imm_size = (byte )(4 - (pr_66 << 1 )); ld->imm_size += (byte )(f & 3 ); if (ld->imm_size != 0 ) { s += ld->imm_size; ld->imm_offset = (byte )(p - (byte *)code); ld->flags |= F_IMM; if ((f & OP_RELATIVE) != 0 ) ld->flags |= F_RELATIVE; } if (s > 15 ) ld->flags |= F_INVALID; return s; }
还有一堆定义可以自己去我改好的antinet里面看,这里不贴了。
此时,我们可以添加上检查是否存在托管调试器的代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 public static bool HasManagedDebugger () byte [] opcodes; byte * pCodeStart; byte * pCodeCurrent; byte * pCodeEnd; ldasm_data ldasmData; bool is64Bit; InitializeManaged(); if (_isDebuggerAttached()) return true ; if (_pIsDebuggerAttached[0 ] == 0x33 && _pIsDebuggerAttached[1 ] == 0xC0 && _pIsDebuggerAttached[2 ] == 0xC3 ) return true ; opcodes = new byte [_isDebuggerAttachedLength]; pCodeStart = _pIsDebuggerAttached; pCodeCurrent = pCodeStart; pCodeEnd = _pIsDebuggerAttached + _isDebuggerAttachedLength; is64Bit = sizeof (void *) == 8 ; while (true ) { uint length; length = Ldasm.ldasm(pCodeCurrent, &ldasmData, is64Bit); if ((ldasmData.flags & Ldasm.F_INVALID) != 0 ) throw new NotSupportedException(); CopyOpcode(&ldasmData, pCodeCurrent, opcodes, (uint )(pCodeCurrent - pCodeStart)); pCodeCurrent += length; if (pCodeCurrent == pCodeEnd) break ; } if (DynamicCrc32.Compute(opcodes) != _isDebuggerAttachedCrc32) return true ; return false ; }
也许有人会问为什么不直接把机器码复制到缓冲区来校验,而是只取其中的Opcode。因为我们要考虑到重定位表的存在,所以只能检测Opcode是否被修改,要检测操作数有没有被修改,实现起来就有点麻烦了。
之前考虑过对整个CLR的.text节进行校验,但是失败了。这部分代码可以去github看我的提交记录,最先几次提交里面有这部分代码,在AntiPatcher.cs 里面,只不过因为失败被注释掉了。
为什么用
1 2 3 if (_isDebuggerAttached()) return true ;
而不是
1 2 3 if (Debugger.IsAttched) return true ;
因为.NET 2.03.5的Debugger.IsAttched的get属性是一个托管方法,存在被直接Patch的可能,会导致在.NET 2.03.5下,托管调试器的检测出现漏洞。